The following acidic galvanic cell is set-up with the following overall cell reaction +7 H2O1) 14 H* (aq) + Cr207 (aq) + 6 Age) → 6 Ag*(aq) + 2 Cr**c@q) V Porous Barrier Pt Ag 0.22 M Na2Cr207 0.25 M Cr(NO3)3 0.20 M AGNO3 If the cell voltage is 0.257 V, what is the pH of the cell?
Please answer the attached question:

![### Acidic Galvanic Cell Setup and pH Determination
#### The Cell Reaction
The acidic galvanic cell is set up with the following overall cell reaction:
\[14 \text{H}^+_{\text{(aq)}} + \text{Cr}_2\text{O}_7^{2-} _{\text{(aq)}}+ 6 \text{Ag}_{\text{(s)}} \rightarrow 6 \text{Ag}^+_{\text{(aq)}} + 2 \text{Cr}^{3+}_{\text{(aq)}} + 7 \text{H}_2\text{O}_{\text{(l)}}\]
#### Diagram Description
The diagram represents a galvanic cell with:
- A porous barrier separating the two half-cells.
- The left half-cell contains a Platinum (Pt) electrode immersed in a solution of 0.22 M Na\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\) and 0.25 M Cr(NO\(_3\))\(_3\).
- The right half-cell contains a Silver (Ag) electrode immersed in a 0.20 M AgNO\(_3\) solution.
- The setup includes a voltmeter (V) connected between the two electrodes, indicating the cell voltage.
#### Problem Statement
"If the cell voltage is 0.257 V, what is the pH of the cell?"
To solve this, you would use the Nernst equation and other relevant electrochemical principles to find the pH of the solution in the galvanic cell based on the given conditions.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F5d4e0e1f-a295-43e5-adcc-ec19e6606cd6%2Fe25b45dd-f9af-4ef4-9760-2e96f44be2fd%2Fx2wlqme.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
The potential across any specified cell is computed using all species' concentration and its standard potential. This expression is also recognized as "Nernst equation" and it also contains the term denoting electrons transferred.
Given:
The temperature is 25 degree Celsius.
The concentration of silver ions is 0.20 M.
The concentration of chromium ions is 0.25 M.
The concentration of chromate ions is 0.22 M.
The cell voltage is 0.257 V.
The given reaction is as follows:
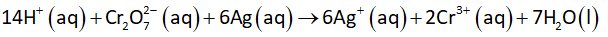
The oxidation half-reaction at anode is shown below.
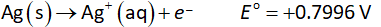
The reduction half-reaction at cathode is shown below.
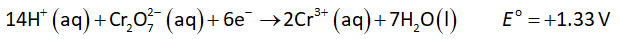
Multiply oxidation-half with 6 and then add oxidation and reduction half-reactions to obtain net reaction as shown below.
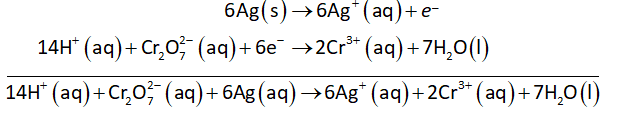
The formula to calculate pH is as follows:
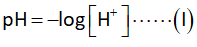
The concentration of hydronium ions is calculated Nernst equation as shown below.
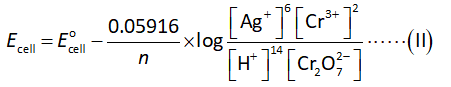
Here,
The number of electrons transfer in the reaction is “n”.
The cell potential is “Ecell”.
The standard cell potential is “”.
It clear from the half-reactions that the number of electrons transferred is 6 (n=6).
The formula to calculate standard cell potential is shown below.
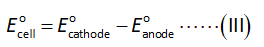
Here,
The electrode potential of cathode is +1.33 V.
The electrode potential of anode is +0.7996 V.
Substitute the values in equation (III).

Suppose the concentration of hydrogen ions is x.
Substitute all known values in equation (II).
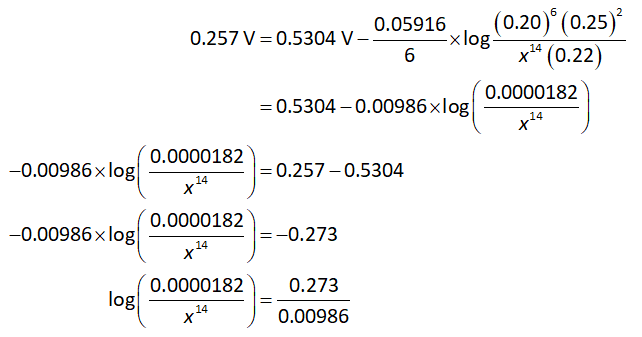
On further solving the equation,
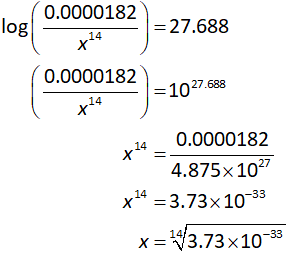
Solving the equation for the value of x:
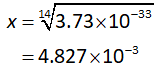
Substitute the concentration of hydrogen ions in equation (I).
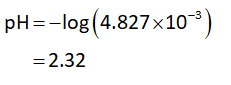
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 12 images









