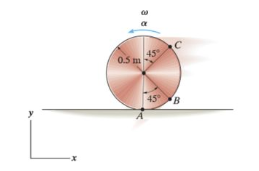
The disk has an angular acceleration a = 7 rad/s² and angular velocity w = 3 rad/s at the instant shown. It does not slip at A. (Figure 1)
The disk has an angular acceleration a = 7 rad/s² and angular velocity w = 3 rad/s at the instant shown. It does not slip at A. (Figure 1)
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Website Transcription:**
---
### Rotational Motion Problem
**Problem Description:**
The disk has an angular acceleration \(\alpha = 7 \, \text{rad/s}^2\) and angular velocity \(\omega = 3 \, \text{rad/s}\) at the instant shown. It does not slip at point \(A\).
**Figure 1:**
The figure illustrates a disk with a radius of \(0.5 \, \text{m}\) rotating about a fixed axis through point \(A\). The disk is positioned such that the line \(AC\) is at a \(45^\circ\) angle with the vertical line through \(A\). The angular velocity \(\omega\) is directed upward, and the angular acceleration \(\alpha\) acts counterclockwise.
**Part A:**
Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point \(C\).
- Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
- Input format: \(a = \_\_\_\_ \, \text{Units}\)
**Part B:**
Determine the direction of the acceleration of point \(C\).
- Express your answer using three significant figures.
- Input format: \(\theta = \_\_\_\_^\circ\), measured counterclockwise from the negative x-axis.
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The disk is shown edge-on with its center marked. The radius extends from the center \(O\) to point \(C\) at a \(45^\circ\) angle. \(A\) is the point on the x-axis where the disk does not slip. Angular velocity \(\omega\) is labeled with a curved arrow at the top of the disk indicating upward direction, and angular acceleration \(\alpha\) is also marked, suggesting anti-clockwise rotation.
This setup is typical for analyzing rotational dynamics and understanding how linear acceleration at a point on a rotating body is determined.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY