Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test. Ho: p=0.89 versus H₁: p=0.89 n = 500, x=440, α = 0.01 Is npo (1-Po) 210? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) OA. Yes, because npo (1-P) = OB. No, because npo (1-P) =
Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test. Ho: p=0.89 versus H₁: p=0.89 n = 500, x=440, α = 0.01 Is npo (1-Po) 210? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) OA. Yes, because npo (1-P) = OB. No, because npo (1-P) =
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-Value Approach**
To test the hypothesis using the P-value approach, we have the following setup:
- Null hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \( p = 0.89 \)
- Alternative hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \( p \neq 0.89 \)
Given data:
- Sample size (\(n\)): 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)): 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)): 0.01
**Verification Requirement**
We need to verify that \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\). Please select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
- A. Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) =\) [ ]
- B. No, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) =\) [ ]
Please compute \(np_0(1 - p_0)\) with the given values to verify the requirement.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4%2F8736135b-8059-4faf-8c43-7a7ce840d924%2Fxovpuf8_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-Value Approach**
To test the hypothesis using the P-value approach, we have the following setup:
- Null hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \( p = 0.89 \)
- Alternative hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \( p \neq 0.89 \)
Given data:
- Sample size (\(n\)): 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)): 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)): 0.01
**Verification Requirement**
We need to verify that \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\). Please select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
- A. Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) =\) [ ]
- B. No, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) =\) [ ]
Please compute \(np_0(1 - p_0)\) with the given values to verify the requirement.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given data,
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
![**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-value Approach**
**Objective:**
Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test.
**Hypotheses:**
- Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \(p = 0.89\)
- Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \(p \neq 0.89\)
**Given:**
- Sample size (\(n\)) = 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)) = 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)) = 0.01
**Step 1: Verify Conditions**
Determine if \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\).
1. Calculate \(np_0(1 - p_0)\):
\[
np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95
\]
Choice A is chosen: *Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95\).*
**Step 2: Find \(\hat{p}\)**
Calculate the sample proportion (\(\hat{p}\)):
- \(\hat{p} = 0.88\)
**Step 3: Find the Test Statistic \(z_0\)**
Calculate the test statistic:
- \(z_0 = -0.72\)
- (Rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
**Step 4: Find the P-value**
The P-value will need to be calculated to three decimal places as needed.
---
**Summary:**
This step-by-step guide helps in conducting a hypothesis test using the P-value approach by verifying the necessary conditions, calculating the sample proportion, finding the test statistic, and determining the P-value. Ensure all values are rounded to the specified precision for accuracy.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4/3157ddfa-7fc0-408c-8bd2-6937eab1a0e0/w8e2lw_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-value Approach**
**Objective:**
Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test.
**Hypotheses:**
- Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \(p = 0.89\)
- Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \(p \neq 0.89\)
**Given:**
- Sample size (\(n\)) = 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)) = 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)) = 0.01
**Step 1: Verify Conditions**
Determine if \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\).
1. Calculate \(np_0(1 - p_0)\):
\[
np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95
\]
Choice A is chosen: *Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95\).*
**Step 2: Find \(\hat{p}\)**
Calculate the sample proportion (\(\hat{p}\)):
- \(\hat{p} = 0.88\)
**Step 3: Find the Test Statistic \(z_0\)**
Calculate the test statistic:
- \(z_0 = -0.72\)
- (Rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
**Step 4: Find the P-value**
The P-value will need to be calculated to three decimal places as needed.
---
**Summary:**
This step-by-step guide helps in conducting a hypothesis test using the P-value approach by verifying the necessary conditions, calculating the sample proportion, finding the test statistic, and determining the P-value. Ensure all values are rounded to the specified precision for accuracy.
Solution
Follow-up Question
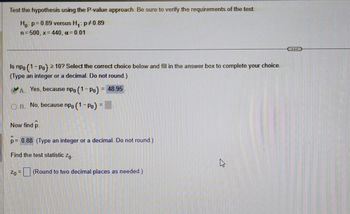
Transcribed Image Text:Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test.
Ho: p=0.89 versus H₁: p#0.89
1
= 500, x= 440, a = 0.01
Is npo (1-Po) ²10? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
A. Yes, because npo (1-Po) = 48.95
OB. No, because npo (1-Po) =
Now find p
p= 0.88 (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
Find the test statistic zo.
Zo = (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
W
---
Solution
Follow-up Question
![**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-Value Approach**
*Question:*
Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test.
- Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \(p = 0.89\)
- Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \(p \neq 0.89\)
- Sample size (\(n\)): 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)): 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)): 0.01
**Verification:**
Check if \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
- A. Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95\). [This option is selected]
- B. No, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = \_\_\_ \).
**Next Step:**
Now find \(\hat{p}\).
- \(\hat{p} = \_\_\_\) (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4/64a688ff-4fc9-4db8-874d-41a1cc6296ed/ld9kadc_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing Using the P-Value Approach**
*Question:*
Test the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test.
- Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \(p = 0.89\)
- Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_1\)): \(p \neq 0.89\)
- Sample size (\(n\)): 500
- Number of successes (\(x\)): 440
- Significance level (\(\alpha\)): 0.01
**Verification:**
Check if \(np_0(1 - p_0) \geq 10\). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
- A. Yes, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = 48.95\). [This option is selected]
- B. No, because \(np_0(1 - p_0) = \_\_\_ \).
**Next Step:**
Now find \(\hat{p}\).
- \(\hat{p} = \_\_\_\) (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman