Tautomers are constitutional isomers that differ in the location of adouble bond and a hydrogen atom. Two tautomers are in equilibriumwith each other. Explain this ?
Reactions of Ethers
Ethers (R-O-R’) are compounds formed by replacing hydrogen atoms of an alcohol (R-OH compound) or a phenol (C6H5OH) by an aryl/ acyl group (functional group after removing single hydrogen from an aromatic ring). In this section, reaction, preparation and behavior of ethers are discussed in the context of organic chemistry.
Epoxides
Epoxides are a special class of cyclic ethers which are an important functional group in organic chemistry and generate reactive centers due to their unusual high reactivity. Due to their high reactivity, epoxides are considered to be toxic and mutagenic.
Williamson Ether Synthesis
An organic reaction in which an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol forms ether is known as Williamson ether synthesis. Alexander Williamson developed the Williamson ether synthesis in 1850. The formation of ether in this synthesis is an SN2 reaction.
Tautomers are constitutional isomers that differ in the location of a
double bond and a hydrogen atom. Two tautomers are in equilibrium
with each other. Explain this ?
The presence of the same counts of the atoms, but different bonding patterns of the molecule leads to the formation of the constitutional isomers. For example, ethanol and dimethyl ether are constitutional isomers. The former has a -OH functional and the latTer has R-O-R functional group. When the relocation of the proton in a molecule leads to the formation of another molecule with the same chemical formula, it is known as the tautomer.
In a pair of tautomers, the position of the protons differs and the positions of the electrons are also interchanged. In this intramolecular proton transfer, the basic skeleton of the molecule remains unchanged. The chemical reaction that is associated with the interconversion of the tautomers is termed as the tautomerization. Notable types of tautomerization are i) keto-enol ii) amide-imide iii) amine-imine.
For example, the removal of the alpha hydrogen from the ketone and the migration of its bonded electrons towards the carbonyl group produces the enol molecule. The ketone and enol form differs only in the position of the hydrogen and each isomer is in equilibrium with the other.
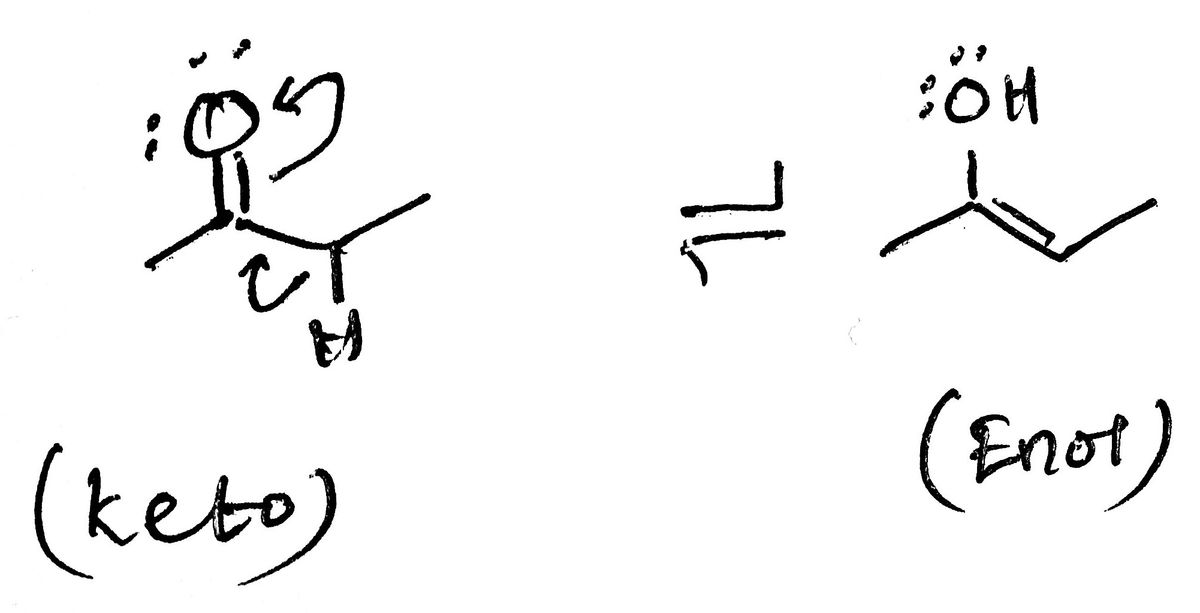
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









