Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:Robert F. Blitzer
ChapterP: Prerequisites: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MCCP: In Exercises 1-25, simplify the given expression or perform the indicated operation (and simplify,...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
![The image contains the following algebraic equation written on lined paper:
\[ 12 - 3(a - 1) = 3 + a \]
This is a linear equation which involves a single variable, \( a \). The goal is typically to solve for \( a \).
### Explanation:
1. **Equation Breakdown**:
- **Left Side**: \( 12 - 3(a - 1) \)
- Here, \( 3 \) is being multiplied by the expression \( (a - 1) \).
- **Right Side**: \( 3 + a \)
- This side adds 3 to the variable \( a \).
2. **Solving the Equation**:
- First, distribute the \(-3\) across the terms inside the parentheses on the left side:
- \( 12 - 3 \times a + 3 = 3 + a \).
- Simplify to \( 12 - 3a + 3 = 3 + a \).
- Combine like terms:
- \( 15 - 3a = 3 + a \).
- Next, isolate \( a \) by adding \( 3a \) to both sides:
- \( 15 = 3 + 4a \).
- Subtract 3 from both sides to isolate terms with \( a \):
- \( 12 = 4a \).
- Finally, divide both sides by 4 to solve for \( a \):
- \( a = 3 \).
The solution to the equation is \( a = 3 \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F4e25a66c-963f-4dcf-b8b4-1372727e9638%2F1ca2581a-8ca3-4321-a5c2-550daf555c01%2Fmo11nd_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:The image contains the following algebraic equation written on lined paper:
\[ 12 - 3(a - 1) = 3 + a \]
This is a linear equation which involves a single variable, \( a \). The goal is typically to solve for \( a \).
### Explanation:
1. **Equation Breakdown**:
- **Left Side**: \( 12 - 3(a - 1) \)
- Here, \( 3 \) is being multiplied by the expression \( (a - 1) \).
- **Right Side**: \( 3 + a \)
- This side adds 3 to the variable \( a \).
2. **Solving the Equation**:
- First, distribute the \(-3\) across the terms inside the parentheses on the left side:
- \( 12 - 3 \times a + 3 = 3 + a \).
- Simplify to \( 12 - 3a + 3 = 3 + a \).
- Combine like terms:
- \( 15 - 3a = 3 + a \).
- Next, isolate \( a \) by adding \( 3a \) to both sides:
- \( 15 = 3 + 4a \).
- Subtract 3 from both sides to isolate terms with \( a \):
- \( 12 = 4a \).
- Finally, divide both sides by 4 to solve for \( a \):
- \( a = 3 \).
The solution to the equation is \( a = 3 \).
Expert Solution
Step 1
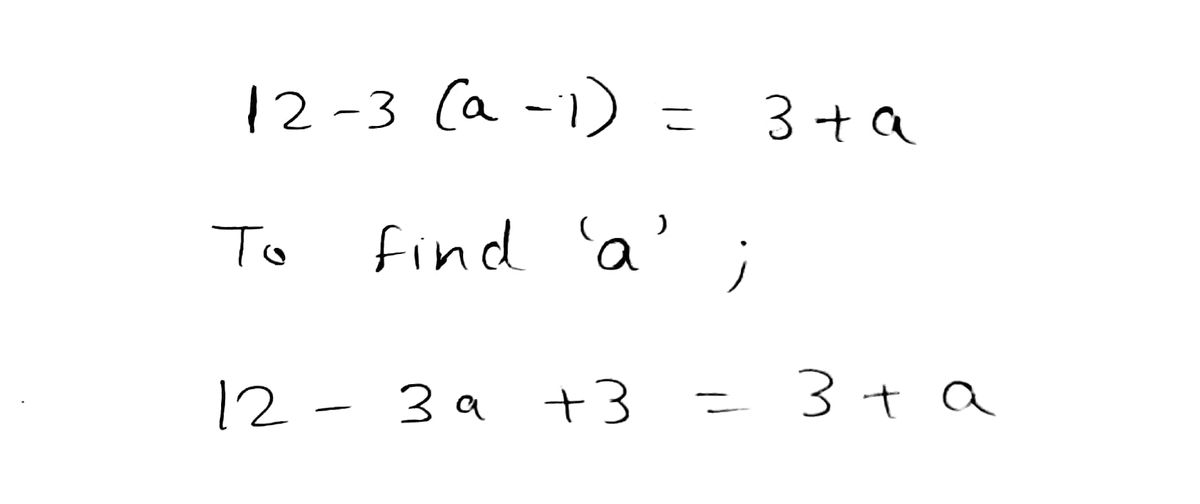
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780135163078
Author:
Michael Sullivan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:
9780980232776
Author:
Gilbert Strang
Publisher:
Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780077836344
Author:
Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education