Synthesis gas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas, is a very important industrial intermediate product. Among other things, synthesis gas is used in the synthesis of methanol, ammonia or synthetic gasoline. Synthesis gas is produced from coal and water at 1200°C: C(s) + H2O(g) --> CO(g) + H2(g) 1) Let K be the equilibrium constant for reaction (1), p be the total pressure and nstart (1 - a) be the mass of H2O in equilibrium, where nstart is the original mass of H2O. Complete the following table: C(s) H2O(s) CO(g) H2(g) sample start nstart 0 0 sample in equilibirium mole fraction in equilibrium 1 partial pressure in equilibrium 2) Write down the formula expression for the equilibrium constant expressed with total pressure p and a. 3) How does it affect the fraction a that has reacted if we increase the pressure by 10kPa by reducing the volume of the container? Justify the answer. 4) The total pressure in the container is increased by 10kPa by adding Ar(g). How does it affect the fraction a which has reacted if we assume that all gases behave as ideal gases? The answer must be justified. 5) How does it affect the fraction a that has reacted if we increase the temperature further.
Synthesis gas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas, is a very important industrial intermediate product. Among other things, synthesis gas is used in the synthesis of methanol, ammonia or synthetic gasoline. Synthesis gas is produced from coal and water at 1200°C:
C(s) + H2O(g) --> CO(g) + H2(g)
1) Let K be the equilibrium constant for reaction (1), p be the total pressure and nstart (1 - a) be the mass of H2O in equilibrium, where nstart is the original mass of H2O.
Complete the following table:
| C(s) | H2O(s) | CO(g) | H2(g) | |
| sample start | nstart | 0 | 0 | |
| sample in equilibirium | ||||
| mole fraction in equilibrium | 1 | |||
| partial pressure in equilibrium |
2) Write down the formula expression for the equilibrium constant expressed with total pressure p and a.
3) How does it affect the fraction a that has reacted if we increase the pressure by 10kPa by reducing the volume of the container? Justify the answer.
4) The total pressure in the container is increased by 10kPa by adding Ar(g). How does it affect the fraction a which has reacted if we assume that all gases behave as ideal gases? The answer must be justified.
5) How does it affect the fraction a that has reacted if we increase the temperature further.
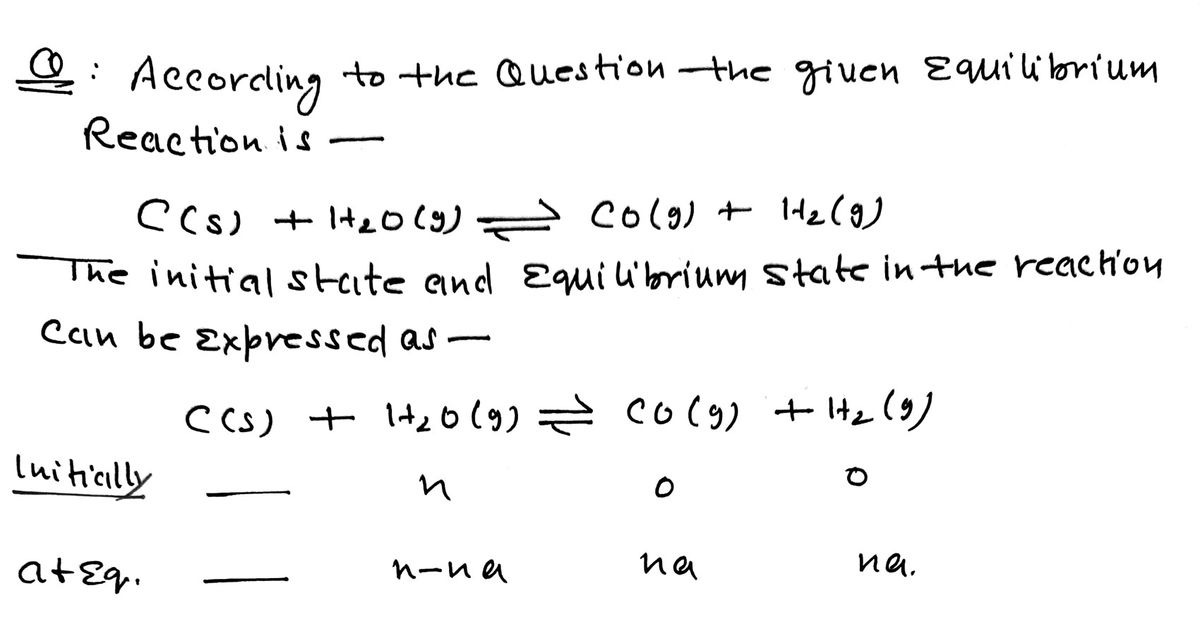
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









