surveying used by anomalles arising from varlations susceptibimty mighi ndicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A andom sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below. Magnetic Susceptibility Readings, centimeter-gram-second x 10-6 (cmg × 10-6) Magnetic Susceptibility OSx< 10 10 sx< 20 20 sx < 30 30 < x < 40 40 SX Number of Readings Estimated Probability 24/120 = 0.20 60/120 = 0.50 24/120 = 0.20 6/120 = 0.05 6/120 = 0.05 Comment "cool" "neutral" 24 60 "warm" 24 "very interesting" "hot spot" 6 Suppose you are working in a "warm" region in which all MS readings are 20 or higher. In this same region, what is the probability that you will find a "hot spot" in which the readings are 40 or higher Jse conditional probability to estimate P(40sx| 20 < x). (Round your answer to three decimal places.) P(40 < x | 20 s x) = |
surveying used by anomalles arising from varlations susceptibimty mighi ndicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A andom sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below. Magnetic Susceptibility Readings, centimeter-gram-second x 10-6 (cmg × 10-6) Magnetic Susceptibility OSx< 10 10 sx< 20 20 sx < 30 30 < x < 40 40 SX Number of Readings Estimated Probability 24/120 = 0.20 60/120 = 0.50 24/120 = 0.20 6/120 = 0.05 6/120 = 0.05 Comment "cool" "neutral" 24 60 "warm" 24 "very interesting" "hot spot" 6 Suppose you are working in a "warm" region in which all MS readings are 20 or higher. In this same region, what is the probability that you will find a "hot spot" in which the readings are 40 or higher Jse conditional probability to estimate P(40sx| 20 < x). (Round your answer to three decimal places.) P(40 < x | 20 s x) = |
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:Magnetic surveying is one technique used by archaeologists to determine anomalies arising from variations in magnetic susceptibility. Unusual changes in magnetic susceptibility might (or might not)
indicate an important archaeological discovery. Let x be a random variable that represents a magnetic susceptibility (MS) reading for a randomly chosen site at an archaeological research location. A
random sample of 120 sites gave the readings shown in the table below.
Magnetic Susceptibility Readings,
centimeter-gram-second x 10-6
Magnetic
Susceptibility
0 < x < 10
10 < x < 20
20 < x < 30
(cmg x 10-6)
Number of
Estimated
Readings
24
Comment
Probability
24/120
60/120
24/120
6/120
6/120
= 0.20
0.50
"сool"
"neutral"
60
"warm"
24
= 0.20
"very interesting"
"hot spot"
30 < x < 40
6.
= 0.05
40 < x
6.
= 0.05
Suppose you are working in a "warm" region in which all MS readings are 20 or higher. In this same region, what is the probability that you will find a "hot spot" in which the readings are 40 or higher?
Use conditional probability to estimate P(40 < x | 20 < x). (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
P(40 < x | 20 < x) =
Expert Solution
Step 1
The formula for calculating the conditional probability is:
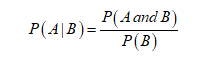
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman