Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm. Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve. (a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm? (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm. Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve. (a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm? (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:10/9/23, 11:06 AM
TABLE V
-2.6
-2.3
.02
.07
.08
.09
0.0019
-34 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0002
-33 0.0005 0.0005 0.0005 0.0004 0.0004 0.0004 0.0004 0.0004 0.0004 0.0003
-3.2 0.0007 0.0007 0.0006 0.0006 0.0006 0.0006 0.0006 0.0005 0.0005 0.0005
-3.1 0.0010 0.0009 0.0009 0.0009 0.0008 0.0008 0.0008 0.0008 0.0007 0.0007
-3.0 0.0013 0,0013 0.0013 0.0012 0.0012 0.0011 0.0011 0.0011 0.0010 0.0010
-2.9 0.0019 0.0018 0,0018 0.0017 0.0016 0.0016 0.0015 0.0015 0.0014 0.0014
-2.8 0.0026 0.0025 0.0024 0.0023 0.0023 0.0022 0.0021 0.0021 0.0020
0.0035 0.0034 0.0033 0.0032 0.0031 0.0030 0.0029 0.0028 0.0027 0.0026
0.0047 0.0045 0.0044 0.0043 0.0041 0.0040 0.0039 0.0038 0.0037 0.0036
0.0062 0.0060 0.0059 0.0057 0.0055 0.0054 0.0052 0.0051 0.0049 0.0048
-2.4 0.0082 0.0080 0.0078 0.0075 0.0073 0.0071 0.0069 0.0068 0.0066 0.0064
-2.3 0.0107 0.0104 0.0102 0.0099 0.0096 0.0094 0.0091 0.0089 0.0087 0.0084
-2.2 0.0139 0.0136 0.0132 0.0129 0.0125 00122 0.0119 0.0116 0.0113 0.0110
-2.1 0.0179 0.0174 0.0170 0.0166 0.0162 0.0158 0.0154 0.0150 0.0146 0.0143
-2.0 0.0228 0.0222 0,0217 0,0212 0.0207 0.0202 0.0197 0.0192 0.0188 0.0183
-1.9 0.0287 0,0281 0.0274 0.0268 0,0262 0.0256 0.0250 0.0244 0.0239 0.0233
-1.8 0.0359 0.0351 0.0344 0.0336 0.0329 0.0322 0.0314 0.0307 0.0301 0.0294
-1.7 0.0446 0.0436 0.0427 0.0418 0.0409 0.0401 0.0392 0.0384 0.0375 0.0367
-1.6 0.0548 0.0537 0.0526 0.0516 0,0505
-1.5 0.0668 0.0655 0.0643 0.0630 0.0618
0.0485 0.0475 0.0465 0.0455
0.0594 0.0582 0.0571 0.0559
0.1
0.2
0.3
.00
Standard Normal Distribution
03 .04 .05
-1.4 0.0808 0.0793 0.0778 0.0764 0.0749 0.0735
-1.3 0.0968 0.0951 0.0934 0,0918 0,0901 0.0885
-1.2 0.1151 0.1131 0.1112 0.1093 0.1075
-1.1
0.1357 0.1335 0.1314 0.1292 0.1271
-1.0 0.1587 0.1562 0.1539 0.1515 0,1492
-0.9 0.1841 0.1814 0.1788 0.1762 0.1736 0.1711 0.1685 0.1660 0.1635 0.1611
-0.8 0.2119 0.2090 0.2061 0.2033 0.2005 0.1977 0.1949 0.1922 0.1894 0.1867
-0.7 0.2420 0.2389 0.2358 0.2327 0.2296 0.2266 0.2236 0.2206 0.2177 02148
-0.6 0.2743 0.2709 0.2676 0.2643 0.2611 0.2578 0.2546 0.2514 02483 0.2451
-0.5 0.3085 0.3050 0.3015 0.2981 0.2946
0.2912 0.2877 0.2843 0.2810 0.2776
-0.4 0.3446 0.3409 0.3372 0.3336 0 3300 0.3264 0.3228 0.3192 0.3156 03121
-0.3
0.3783 0.3745 0.3707 0.3669 0.3632 0.3594 0.3557 0.3520 0.3483
<-0.2 0.4207 0.4168 0.4129 0.4090 04052
0.3974 0.3936 0.3897 0.3859
-0.1 0.4602 0.4562 0.4522 0.4483 0.4443 0.4404 0.4364 0.4325 0.4286 0.4247
0.5000
0,4920 0,4880 0.4840
04761 04721 0.4681 0.4641
0.5000 05040 0.5080 0.5120 0.5160 0.5199 05239
0.5279 05319 0.5359
0.5398 0.5438 0.5478 0.5517 0.5557 0.5590 0.5636 0.5675 0.571 0.5753
0.5832 0.5871 0.5910 0.5948 0.5987 0.6026 0.6064 0.6103 0.6141
06179 0.6217 06255 0.6293 06331 0.6368 0.6406 0.6443 0.6480 0.6517
0.4 0.6554 0,6591 0.6628 0.6664
0.6700 0.6736 0.6772 0.6808 0.6844 0.6879
0.6985 0,7019 0.7054
0.7123 0.7157 0.7190 0.7224
0.7324 0.7357 0.7389 0.7422 0.7454
0.7486 0.7517 0.7549
0.7 0.7580 0.7611 0.7642 0.7673 0.7704 0.7734 0.7764 0.7794 0.7823 0.7852
0.8 0.7881 0.7910 0.7939 0.7967 0.7995 0.8023 0.8051 0.8078 0.8106 0.8133
0.9 0.8159 0.8186 0.8212 0.8238 0.8264 0.8289 0.8315 0.8340 0.8365 0.8389
1.0 0.8413 0.8438 0.8461
0.8531 0.8554 0.8577 0.8599 0.8621
1.1 0.8643 0.8665 0.8686 0.8708 0.8729 0.8749 0.8770 0.8790 08810 0.8830
1.2 0.8849 0.8869 0.8888 0,8907 0.8925 0.8944 0.8962 0.8980 08997 0.9015
1.3 0.9032 0.9049 0.9066 0.9082 0.9099 0.9115 0.9131 0.9147 0.9162 0.9177
1.4 0.9192 0.9207 0.9222 0.9236 0.9251 0.9265 0.9279 0.9292 0.9306 0.9319
1.5 0.9332 0.9345 0.9357 0.9370 0,9382 0.9394 0.9406 09418 0.9429 0.9441
1.6 0.9452 0.9463 0.9474 0.9484 0.9495 0.9505 0.9515 0.9525 0.9535 0.9545
1.7 0.9554 0.9564 0.9573 0.9582 0.9591 0.9599 0.9608 0.9616 0.9625 0.9633
1.8 0,9641 0.9649 0.9656 0.9664 0.9671 0.9678 0.9686 0.9693 0.9699 0.9706
1.9 0.9713 0.9719 0.9726 0.9732 0.9738 0.9744 0.9750 0.9756 0.9761 0.9767
0.5 0.6915 0,6950
0.6 0.7257
0.8508
31
3.2
.00
90⁰
Tables of Areas under the Normal Curve
0.9890
2.0 0.9772 0.9778 0.9783 0.9788 0.9793 0.9798 0.9803 0.9808 0.9812
2.1 0.9821 0.9826 0.9830 0.9834 0.9838 0.9842 0.9846 0.9850 0.9854
22 0.9861 0.9864 0.9868 0.9871 0.9875 0.9878 0.9881 0.9884 0.9887
2.3 0.9893 0.9896 0.9898 0.9901 0.9904 0.9900 0.9909 0.9911 0.9913 0.9916
2.4 0.9918 0.9920 0.9922 0.9925 0.9927 0.9929 0.9931 0.9932 0.9934 0.9936
2.5 0.9938 0.9940 0.9941 0.9943 0.9945 0.9946 0.9948 0.9949 0.9951 0.9952
26 0.9953 0.9955 0.9956 0.9957 0.9959 0.9960 0.9961 0.9962 0.9963 0.9964
27 0.9965 0.9966 0.9967 0.9968 0.9969 0.9970 0.9971 0.9972 0.9973 0.9974
2.8 0.9974 0.9975 0.9976 0.9977 0.9977 0.9978 0.9979 0.9979 09980 0.9981
2.9 0.9981 0.9982 0.9982 0.9983 0.9984 0.9984 0.9985 0.9985 09986 0.9986
L666'0
3.0 0.9987 0.9987 0.9987 0.9988 0.9988 0.9989 0.9989 0.9989 0.9990 0.9990
0.9990 0.9991 0.9991 0.9991 0,9992 0.9992 0.9992 0.9992 0.9993 0.9993
0.9993 0.9993 0.9994 0.9994 0.9994 0.9994 0.9994 0.9995 0.9995 0.9995
3.3 0.9995 0.9995 0.9995 0.9996 0.9996 0.9996 0.9996 0.9996 0.9996 0.9997
3.4 0.9997 0.9997 0.9997
0.9997 0.9997 0.9998
0.9997 0.9997
0.9997
.01
.02
.04
.06
07
.08
.09
03
0.0721 0.0708 0.0694 0.0681
0.0869 0.0853 0.0838 0.0823
0.1038 0.1020 0.1003 0.0985
0.1251 0.1230 0.1210 0.1190 0.1170
0.1469 0.1446 0.1423 0.1401 0.1379
.05
0.9817
0.9857

Transcribed Image Text:Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm.
Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve.
(a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
Step 1: Information given is
Mean()=22
standard deviation()=0.06
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm.
Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve.
(a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?
0.0475 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(b) Any rods that are shorter than 21.86 cm or longer than 22.14 cm are discarded. What proportion of rods will be discarded?
0.0196 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(c) Using the results of part (b), if 5000 rods are manufactured in a day, how many should the plant manager expect to discard?
98
(Use the answer from part b to find this answer. Round to the nearest integer as needed.)
(d) If an order comes in for 10,000 steel rods, how many rods should the plant manager expect to manufacture if the order states that all rods must be between 21.9 cm and 22.1 cm?
(Round up to the nearest integer.)
Solution
Follow-up Question
![Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeters (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm.
### Questions and Solutions:
(a) **What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?**
- Answer: 0.0475 (rounded to four decimal places).
(b) **Any rods that are shorter than 21.86 cm or longer than 22.14 cm are discarded. What proportion of rods will be discarded?**
- Answer: 0.0196 (rounded to four decimal places).
(c) **Using the results of part (b), if 5000 rods are manufactured in a day, how many should the plant manager expect to discard?**
- Answer: 98 rods (use the answer from part b and round to the nearest integer).
(d) **If an order comes in for 10,000 steel rods, how many rods should the plant manager expect to manufacture if the order states that all rods must be between 21.9 cm and 22.1 cm?**
- Solution: [Round up to the nearest integer.]
**Note:** There is an icon mentioned to view a table of areas under the normal curve, likely used to find the probabilities needed for these calculations.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4/e49bfde2-bbf2-47b2-9271-ee7c0ca53f38/efhv8qq_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeters (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm.
### Questions and Solutions:
(a) **What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?**
- Answer: 0.0475 (rounded to four decimal places).
(b) **Any rods that are shorter than 21.86 cm or longer than 22.14 cm are discarded. What proportion of rods will be discarded?**
- Answer: 0.0196 (rounded to four decimal places).
(c) **Using the results of part (b), if 5000 rods are manufactured in a day, how many should the plant manager expect to discard?**
- Answer: 98 rods (use the answer from part b and round to the nearest integer).
(d) **If an order comes in for 10,000 steel rods, how many rods should the plant manager expect to manufacture if the order states that all rods must be between 21.9 cm and 22.1 cm?**
- Solution: [Round up to the nearest integer.]
**Note:** There is an icon mentioned to view a table of areas under the normal curve, likely used to find the probabilities needed for these calculations.
Solution
Follow-up Question
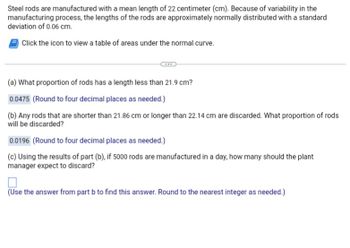
Transcribed Image Text:Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the
manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard
deviation of 0.06 cm.
Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve.
(a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?
0.0475 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(b) Any rods that are shorter than 21.86 cm or longer than 22.14 cm are discarded. What proportion of rods
will be discarded?
0.0196 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(c) Using the results of part (b), if 5000 rods are manufactured in a day, how many should the plant
manager expect to discard?
(Use the answer from part b to find this answer. Round to the nearest integer as needed.)
Solution
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Steel rods are manufactured with a mean length of 22 centimeter (cm). Because of variability in the manufacturing process, the lengths of the rods are approximately normally distributed with a standard deviation of 0.06 cm.
Click the icon to view a table of areas under the normal curve.
(a) What proportion of rods has a length less than 21.9 cm?
0.0475 (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
(b) Any rods that are shorter than 21.86 cm or longer than 22.14 cm are discarded. What proportion of rods will be discarded?
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman