Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 36.2 mL. 8 g x²² collected x gas Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. water y chemical reaction
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced. Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be 36.2 mL. 8 g x²² collected x gas Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the reaction conditions and the nature of the gases. water y chemical reaction
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter5: Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.108PAE
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube is measured to be
36.2 mL.
x10
X
y
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Ś
collected
gas
Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the
reaction conditions and the nature of the gases.
|| g
water
chemical
reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
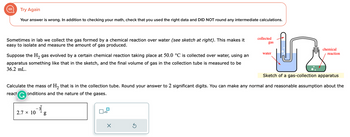
Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
Sometimes in lab we collect the gas formed by a chemical reaction over water (see sketch at right). This makes it
easy to isolate and measure the amount of gas produced.
Suppose the H₂ gas evolved by a certain chemical reaction taking place at 50.0 °C is collected over water, using an
apparatus something like that in the sketch, and the final volume of gas in the collection tube measured to be
36.2 mL.
2.7 × 10
_3__8
g
Sketch of a gas-collection apparatus
Calculate the mass of H₂ that is in the collection tube. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. You can make any normal and reasonable assumption about the
react G onditions and the nature of the gases.
x10
X
collected
Ś
gas
water
chemical
reaction
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning