Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
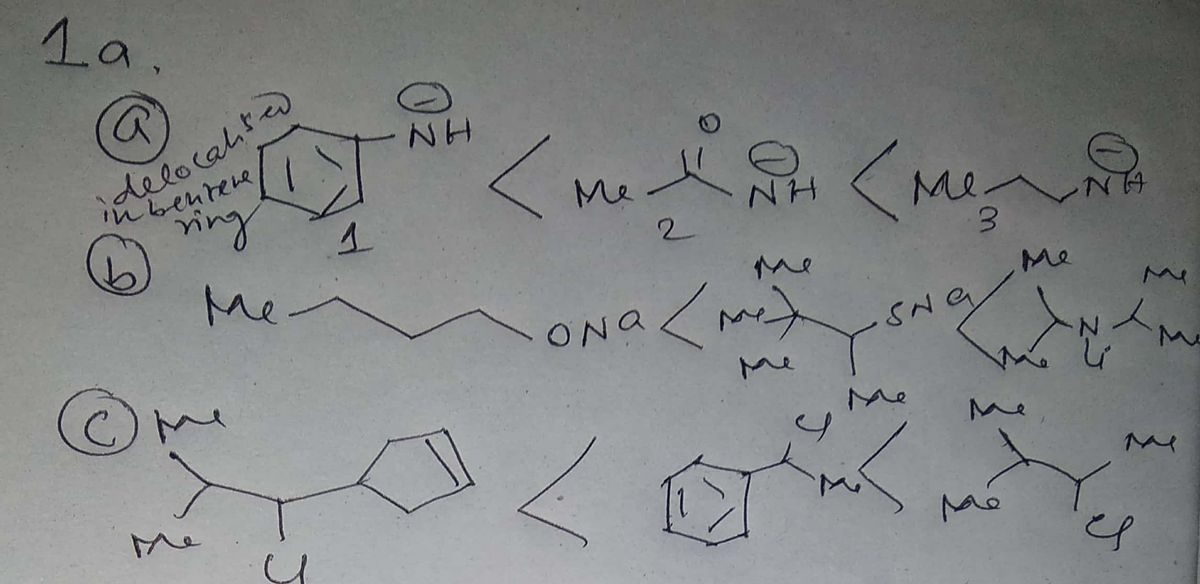
1c.

Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Understanding SN2 Reaction Rates: Ranking Molecules by Reactivity**
**Introduction:**
In this exercise, you will examine several sets of molecular structures and rank them according to their reactivity in SN2 reactions. The SN2 (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) reaction is influenced by various factors including the steric environment, leaving group ability, and nucleophile strength.
**Objective:**
Rank the following sets of molecules in order of increasing SN2 reaction rate (1 = slowest; 3 = fastest).
### **Molecule Sets and Structures:**
**Set a:**
1. An anion with a benzene ring attached to an NH group.
2. An anion with an aliphatic chain involving a NH group.
3. An anion with a carbonyl group (MeC=O) attached to NH.
**Set b:**
1. An anion with a sulfur group (SNa) attached to a tertiary carbon with methyl groups.
2. An anion with an aliphatic chain and ONa group.
3. A lithium anion attached to a tertiary carbon with methyl groups.
**Set c:**
1. A benzene ring attached to a chloromethyl group.
2. An alkyl chloride with two methyl groups.
3. A cyclopentyl chloride.
**Set d:**
1. A vinyl chloride.
2. A vinyl bromide with a methyl group.
3. A secondary iodide with two methyl groups.
**Set e:**
1. A CF3SO2O- group attached to a cyclopentyl ring.
2. A bromocyclopentane.
3. A cyclopentylamine.
### **Analysis Guide:**
- **Steric Effects:** Bulky groups surrounding the reactive site can hinder nucleophilic attack, slowing the SN2 reaction.
- **Leaving Group Ability:** Good leaving groups, such as iodide or tosylate, favor faster reactions compared to poorer leaving groups like chloride.
- **Nucleophile Strength:** Stronger nucleophiles typically increase the rate of SN2 reactions.
### **Conclusion:**
Analyze each set based on the outlined criteria. Consider how the structures influence the SN2 reaction rate and arrange them from slowest to fastest to understand underlying chemical principles.
**End of Exercise**
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY