Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
![---
**Topic: Logarithmic Differentiation**
Use logarithmic differentiation to find \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) for the function:
\[
y = \frac{12xe^x}{\sqrt{3x + 2}}
\]
---
**Explanation:**
Logarithmic differentiation is a technique used to differentiate functions in the form of products or quotients. It simplifies the differentiation process by taking the natural logarithm of both sides, allowing for easier application of the chain rule and product/quotient rules.
1. Take the natural logarithm of both sides: \(\ln(y) = \ln\left(\frac{12xe^x}{\sqrt{3x + 2}}\right)\).
2. Apply logarithmic properties to simplify: \(\ln(y) = \ln(12) + \ln(x) + \ln(e^x) - \ln(\sqrt{3x + 2})\).
3. Differentiate implicitly with respect to \(x\): \(\frac{1}{y} \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{1}{x} + 1 - \frac{1}{2(3x + 2)} \cdot 3\).
4. Solve for \(\frac{dy}{dx}\): \(\frac{dy}{dx} = y \left(\frac{1}{x} + 1 - \frac{3}{2(3x + 2)}\right)\).
5. Substitute back for \(y\) using the original function: \(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{12xe^x}{\sqrt{3x + 2}} \left(\frac{1}{x} + 1 - \frac{3}{2(3x + 2)}\right)\).
This method is especially useful for complex functions like products and quotients of exponentials, polynomials, and roots.
---](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F8b02c858-36fd-4bb4-a48f-d14b7c311887%2F79609686-7d1a-432f-bfda-8b2267992ca7%2Fl5n7at_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
We do logarithmic differentiation by taking log on both sides of equation and then differentiate w. r. t. x to find dy/dx
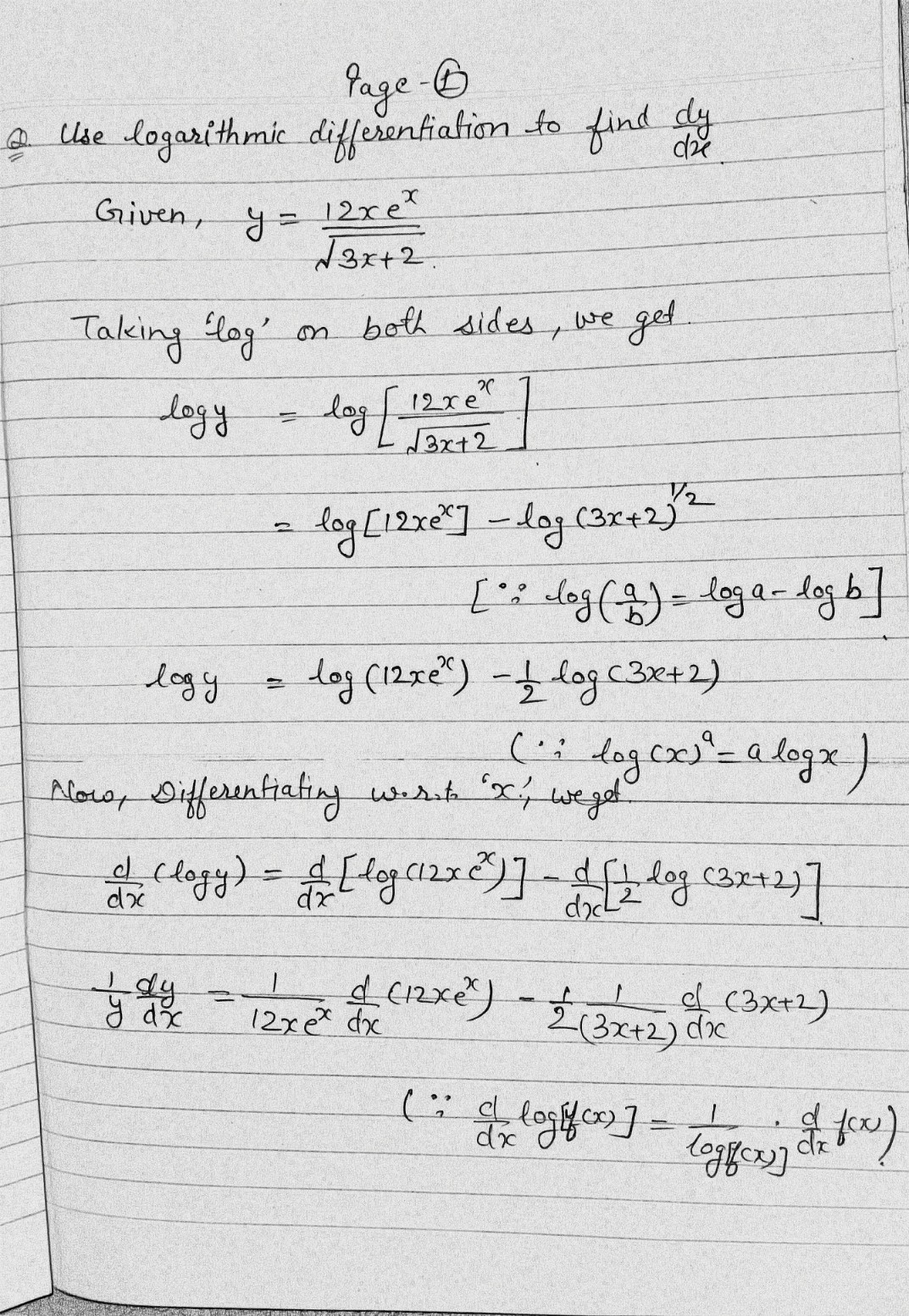
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









