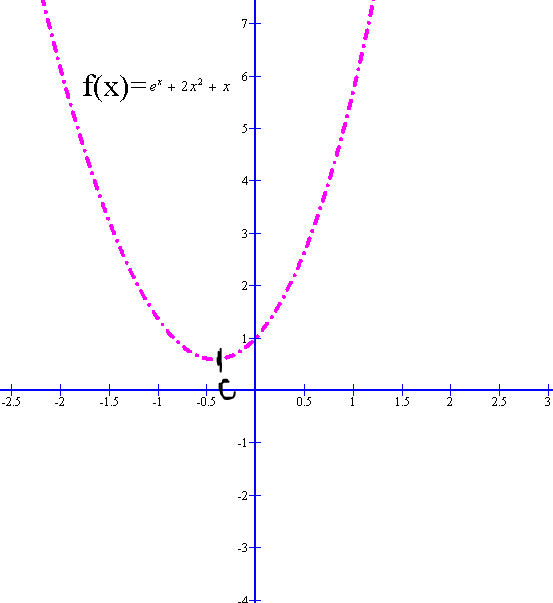
Show that the following function has exactly one critical point. Use Newton’s method to obtain an approximation to the critical point of f(x), by calculating the first iteraton x1 with x0=0. f(x)=ex+2x2+x
Minimization
In mathematics, traditional optimization problems are typically expressed in terms of minimization. When we talk about minimizing or maximizing a function, we refer to the maximum and minimum possible values of that function. This can be expressed in terms of global or local range. The definition of minimization in the thesaurus is the process of reducing something to a small amount, value, or position. Minimization (noun) is an instance of belittling or disparagement.
Maxima and Minima
The extreme points of a function are the maximum and the minimum points of the function. A maximum is attained when the function takes the maximum value and a minimum is attained when the function takes the minimum value.
Derivatives
A derivative means a change. Geometrically it can be represented as a line with some steepness. Imagine climbing a mountain which is very steep and 500 meters high. Is it easier to climb? Definitely not! Suppose walking on the road for 500 meters. Which one would be easier? Walking on the road would be much easier than climbing a mountain.
Concavity
In calculus, concavity is a descriptor of mathematics that tells about the shape of the graph. It is the parameter that helps to estimate the maximum and minimum value of any of the functions and the concave nature using the graphical method. We use the first derivative test and second derivative test to understand the concave behavior of the function.
Show that the following function has exactly one critical point.
Use Newton’s method to obtain an approximation to the critical point of f(x), by calculating the first iteraton x1 with x0=0.
f(x)=ex+2x2+x
Newton-Raphson method or Newton's method is one of the most widely used techniques to find the root of a non-linear equation.
This method requires an initial value, which serves as an initial guess of the root.
the root is approximated after several iterations which is given by:
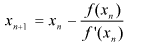
where n+1 is the no. of iterations
xn : previous or assumed value of the root
xn+1: next value of the root
f(x) is the given function
and f'(x) is the derivative of function f(x)
critical points of a function f(x) are the points where slope or f'(x)=0.
here in this graph point, C is the critical point
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images









