Several ice cubes (ρi = 0.9167 g/cm3) of total volume Vi = 205 cm3 and temperature 273.15 K (0.000 °C) are put into a thermos containing Vt = 680 cm3 of tea at a temperature of 313.15 K, completely filling the thermos. The lid is then put on the thermos to close it. Assume that the density and the specific heat of the tea is the same as it is for fresh water (ρw = 1.00 g/cm3, c = 4186 J/kgK). a. Calculate the equilibrium temperature TE in K of the final mixture of tea and water. b. Calculate the magnitude of the total heat transferred QT in J from the tea to the ice cubes.
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
Several ice cubes (ρi = 0.9167 g/cm3) of total volume Vi = 205 cm3 and temperature 273.15 K (0.000 °C) are put into a thermos containing Vt = 680 cm3 of tea at a temperature of 313.15 K, completely filling the thermos. The lid is then put on the thermos to close it. Assume that the density and the specific heat of the tea is the same as it is for fresh water (ρw = 1.00 g/cm3, c = 4186 J/kgK).
a. Calculate the equilibrium temperature TE in K of the final mixture of tea and water.
b. Calculate the magnitude of the total heat transferred QT in J from the tea to the ice cubes.
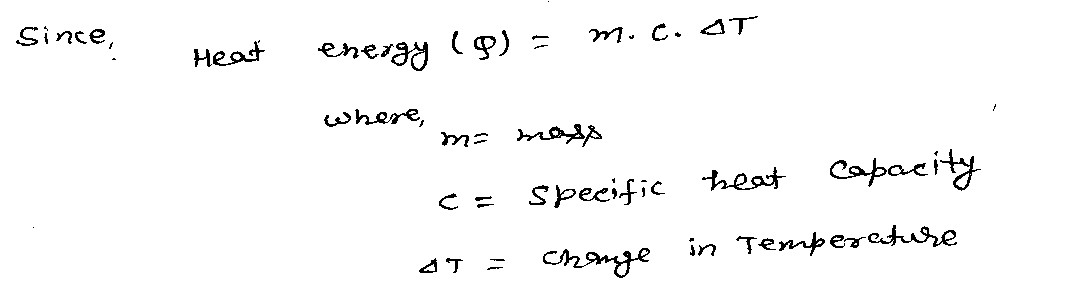
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









