SEPR based geometries for the following compounds, and name both the electronic and molecular geometries: b) H-C N: c) ä-c-a: CI O-0–0 CI CI-C-CI N. H–C-N 1 ČI 6. 10 H–C=N H 'N. CI, 0=0 7 8. CI 3 4 11 12 VSEPR: Electronic Geometry: Molecular Geometry:
Formal Charges
Formal charges have an important role in organic chemistry since this concept helps us to know whether an atom in a molecule is neutral/bears a positive or negative charge. Even if some molecules are neutral, the atoms within that molecule need not be neutral atoms.
Polarity Of Water
In simple chemical terms, polarity refers to the separation of charges in a chemical species leading into formation of two polar ends which are positively charged end and negatively charged end. Polarity in any molecule occurs due to the differences in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Water, as we all know has two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom. As oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen thus, there exists polarity in the bonds which is why water is known as a polar solvent.
Valence Bond Theory Vbt
Valence bond theory (VBT) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. It gives a quantum mechanical approach to the formation of covalent bonds with the help of wavefunctions using attractive and repulsive energies when two atoms are brought from infinity to their internuclear distance.
![**Question**: Determine the geometries for the following compounds, and name both the electronic and molecular geometry.
**Compounds**:
a) \[ \overset{\cdot \cdot}{\text{O}}\overset{\cdot \cdot}{\text{O}}-\overset{\cdot \cdot}{\text{O}}=\overset{\cdot \cdot}{\text{O}} \] (Peroxide ion with additional electrons shown as dots)
b) \[ \text{H} - \text{C} \equiv \text{N} \] (Hydrogen cyanide)
c)
```
..
:Cl:
|
:Cl-C-Cl:
|
:Cl:
..
```
(Chloromethane with lone pairs represented as dots around chlorine atoms)
**Diagrams Explained**:
- **Diagram a**: Represents a peroxide ion (O₂²⁻). The Lewis structure shows each oxygen atom connected by a single bond to one oxygen and a double bond to the other, with lone pairs on each oxygen atom.
- **Diagram b**: Shows a molecule of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) with a single bond between hydrogen and carbon and a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen.
- **Diagram c**: Depicts chloromethane (CCl₄), a tetrahedral molecule where carbon is single-bonded to four chlorine atoms, with lone pairs on each chlorine.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1bfdb6c6-6fc3-4de6-b47d-25e0ae945ba0%2F7b69c5a3-28bc-4dbc-b4f7-96cb1ee64c18%2Fbn7fxua_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
![**VSEPR Geometries for Selected Compounds**
Analyze the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) based geometries for the following compounds. Identify both their electronic and molecular geometries:
### Compound Representations:
1. **a) \[*SO₂*; *O*--*S*--*O* with lone pairs on sulfur*\]**
- Representation: A bent structure with a central sulfur atom bonded to two oxygen atoms, including lone pairs on the sulfur.
2. **b) \[*HCN*; *H*--*C*≡*N*\]**
- Representation: A linear structure with hydrogen bonded to carbon, which is triple-bonded to nitrogen.
3. **c) \[*CCl₃⁻*; *Cl*--*C*--*Cl*, with a third *Cl* and a lone pair on the central carbon*\]**
- Representation: A trigonal pyramidal structure with a central carbon atom bonded to three chlorine atoms and a lone pair.
### Diagram Explanations:
- **Molecules 1 to 4** show variations of bent and linear geometries for compounds involving combinations of elements like sulfur and oxygen.
- **Molecules 5 to 8** include structures with hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen, reflecting linear geometries due to the presence of triple bonds (e.g., H--C≡N).
- **Molecules 9 to 12** involve chlorine atoms around a central carbon, showing variations in geometry due to different configurations of chlorine atoms and lone pairs:
- **9**: Tetrahedral structure with four chlorine atoms arranged around a central carbon with no lone pairs.
- **10**: Also tetrahedral with a similar arrangement to 9.
- **11**: Illustrated with lone pairs, possibly representing anion or expanded valence scenario.
- **12**: Similar to 11, showcasing potential deviations from ideal angles due to lone pairs.
Each molecule varies in its electronic geometry (based on the number of electron pairs) and molecular geometry (the arrangement of atoms), emphasizing how VSEPR theory helps predict shapes.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1bfdb6c6-6fc3-4de6-b47d-25e0ae945ba0%2F7b69c5a3-28bc-4dbc-b4f7-96cb1ee64c18%2Ffph8jwh_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
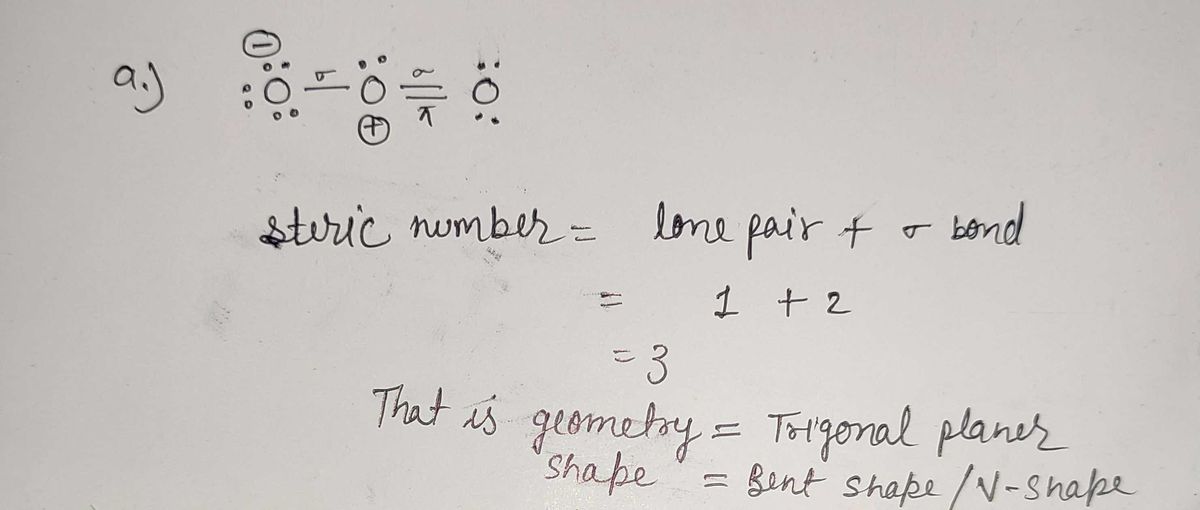
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









