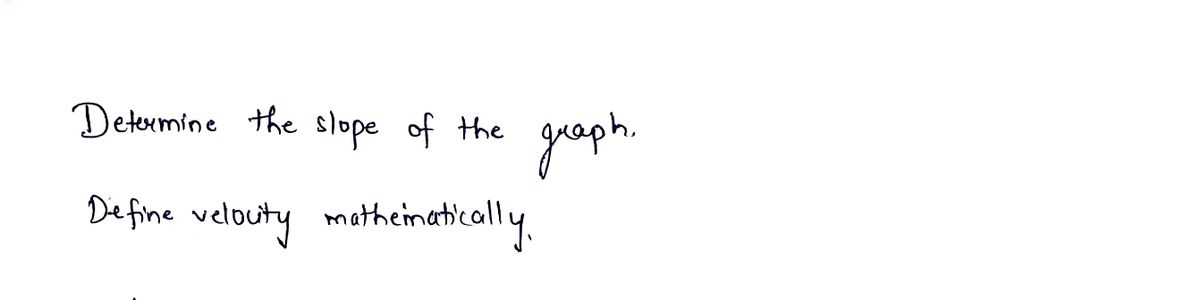
Review: Graphing Kinematics Definitions: Complete the definitions for the following quantities. Distance (Ad): A Scuder, quantity that refers to how much greene an object Position (d): Where Sumeen /object has been put d d₂ di at d Displacement (Ad): vector quantity that refers to the totuus. disfarce including the objects Change in position Determine the slope of the graph. t₁ Define velocity mathematically: Summary: For any complicated graph, divide it up into sections at every point where its behaviour changes. Describe each section mathematically. O The slope of a d-t graph represents A Summary Graph Questions During which interval(s) is the object a) at rest B d) moving quickest g) furthest from the start A-7B and b) moving forward e) moving slowest D-7E D -0 SPH4U E c) moving backward f) at zero displacement
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
In classical mechanics, kinematics deals with the motion of a particle. It deals only with the position, velocity, acceleration, and displacement of a particle. It has no concern about the source of motion.
Linear Displacement
The term "displacement" refers to when something shifts away from its original "location," and "linear" refers to a straight line. As a result, “Linear Displacement” can be described as the movement of an object in a straight line along a single axis, for example, from side to side or up and down. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Linear displacement is usually measured in millimeters or inches and may be positive or negative.

Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









