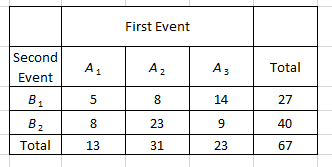
Refer to the following table. First Event Second Event A1 A2 A3 Total B1 5 8 14 27 B2 8 23 9 40 Total 13 31 23 67 Click here for the Excel Data File a. Determine P(A3). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) b. Determine P(A1 | B1). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) c. Determine P(B1 and A2). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Inverse Normal Distribution
The method used for finding the corresponding z-critical value in a normal distribution using the known probability is said to be an inverse normal distribution. The inverse normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with a family of two parameters.
Mean, Median, Mode
It is a descriptive summary of a data set. It can be defined by using some of the measures. The central tendencies do not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset. However, they give a summary of the data set. The central tendency or measure of central tendency is a central or typical value for a probability distribution.
Z-Scores
A z-score is a unit of measurement used in statistics to describe the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean, measured with reference to standard deviation from the mean. Z-scores are useful in statistics because they allow comparison between two scores that belong to different normal distributions.
Refer to the following table.
| First |
|||||||
| Second Event | A1 | A2 | A3 | Total | |||
| B1 | 5 | 8 | 14 | 27 | |||
| B2 | 8 | 23 | 9 | 40 | |||
| Total | 13 | 31 | 23 | 67 | |||
Click here for the Excel Data File
a. Determine P(A3). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
b. Determine P(A1 | B1). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
c. Determine P(B1 and A2). (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Given table ,
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









