reasonably regarded as a a sample from a standard deviation
Inverse Normal Distribution
The method used for finding the corresponding z-critical value in a normal distribution using the known probability is said to be an inverse normal distribution. The inverse normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution with a family of two parameters.
Mean, Median, Mode
It is a descriptive summary of a data set. It can be defined by using some of the measures. The central tendencies do not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset. However, they give a summary of the data set. The central tendency or measure of central tendency is a central or typical value for a probability distribution.
Z-Scores
A z-score is a unit of measurement used in statistics to describe the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean, measured with reference to standard deviation from the mean. Z-scores are useful in statistics because they allow comparison between two scores that belong to different normal distributions.

Given:
In a sample of 400 male students, it was observed that they have a mean height (of 55+18) inches.
Hence,
The null and alternative hypotheses can be written as:
Ho:
Vs
H1:
As the alternative hypothesis includes a "not equal to" sign, the test can be considered a two-tailed test.
The test statistic is calculated as:
Use Excel to determine the P-value for z = 107.69. Use the function =NORM.S.DIST(107.69,FALSE). The screenshot is shown below"
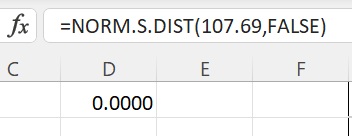
For a two-tailed test, the P-value will be 0.0000.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









