Question 7 Solubility Rules for Some Ionic Compounds in Water Seluble compounds Almost all salts of Na", K, NH4 Salts of nitrate (NO, ), chlorate (CIO, ), perchlorate (CIO,), acetate (CH3 CO,) Almost all salts of Cl, Br, I Exceptions (not soluble): halides of Ag, Hg, , Ph2+ Salts containing F Exceptions (not soluble): fluorides of Mg+, Ca, Sr+ Ba+. Pb?+ Salts of sulfate (So,) Exceptions (not soluble): sulfates of Ca+, Sr+, Ba", Pb2, Ag Insoluble compounds Most salts of carbonate (CO,), phosphate (PO,), oxalate (C,0,), chromate (Cro,), sulfide (S-) Exceptions (soluble): salts of NH* and the alkali metal cations, and Bas Most metal hydroxides and oxides Exceptions (soluble): alkali metal hydroxides and Ba(OH)2 and Sr(OH), A. Write the net ionic equation for the following molecular equation. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) +K2CO3 (aq) PbCO3(s) + 2KN03(aq) (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + B. The following molecular equation represents the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and zinc chloride are combined. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + ZnCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (s) + Zn(NO3)2 (aq) Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + C. When aqueous solutions of iron(III) sulfate and sodium carbonate are combined, solid iron(III) carbonate and a solution of sodium sulfate are formed. The net ionic equation for this reaction is: (Use the solubility rules provided in the OWL Preparation Page to determine the solubility of compounds.) Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box not needed leave it blank.
Question 7 Solubility Rules for Some Ionic Compounds in Water Seluble compounds Almost all salts of Na", K, NH4 Salts of nitrate (NO, ), chlorate (CIO, ), perchlorate (CIO,), acetate (CH3 CO,) Almost all salts of Cl, Br, I Exceptions (not soluble): halides of Ag, Hg, , Ph2+ Salts containing F Exceptions (not soluble): fluorides of Mg+, Ca, Sr+ Ba+. Pb?+ Salts of sulfate (So,) Exceptions (not soluble): sulfates of Ca+, Sr+, Ba", Pb2, Ag Insoluble compounds Most salts of carbonate (CO,), phosphate (PO,), oxalate (C,0,), chromate (Cro,), sulfide (S-) Exceptions (soluble): salts of NH* and the alkali metal cations, and Bas Most metal hydroxides and oxides Exceptions (soluble): alkali metal hydroxides and Ba(OH)2 and Sr(OH), A. Write the net ionic equation for the following molecular equation. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) +K2CO3 (aq) PbCO3(s) + 2KN03(aq) (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + B. The following molecular equation represents the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and zinc chloride are combined. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + ZnCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (s) + Zn(NO3)2 (aq) Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) + C. When aqueous solutions of iron(III) sulfate and sodium carbonate are combined, solid iron(III) carbonate and a solution of sodium sulfate are formed. The net ionic equation for this reaction is: (Use the solubility rules provided in the OWL Preparation Page to determine the solubility of compounds.) Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box not needed leave it blank.
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
I need help understanding how to do this homework question. I've been out sick so I don't even know how to even begin to attempt this question.

Transcribed Image Text:Question 7
Solubility Rules for Some Ionic Compounds in Water
Soluble compounds
Almost all salts of Na*, K, NH4
Salts of nitrate (NO, ), chlorate (CIO; ), perchlorate (CI0,), acetate (CH3 CO,)
Almost all salts of Cl", Br, I
Exceptions (not soluble): halides of Ag, Hg, +, Ph2+
Salts containing F
Exceptions (not soluble): fluorides of Mg+, Ca, Sr+ Ba+ Pb?+
Salts of sulfate (So,)
Exceptions (not soluble): sulfates of Ca+, Sr+, Ba, Ph2, Ag
Insoluble compounds
Most salts of carbonate (CO,), phosphate (PO,), oxalate (C20,), chromate (Cro,), sulfide (S)
Exceptions (soluble): salts of NH4" and the alkali metal cations, and Bas
Most metal hydroxides and oxides
Exceptions (soluble): alkali metal hydroxides and Ba(OH)2 and Sr(OH)2
A. Write the net ionic equation for the following molecular equation.
Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CO3 (aq) PbCO3 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
(Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.)
B. The following molecular equation represents the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and zinc chloride are combined.
Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + ZnCl2 (aq) → PbCl (s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq)
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction.
(Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.)
C. When aqueous solutions of iron(III) sulfate and sodium carbonate are combined, solid iron(III) carbonate and a solution of sodium sulfate are formed. The net ionic equation for this reaction is:
(Use the solubility rules provided in the OWL Preparation Page to determine the solubility of compounds.)
Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box
not needed leave it blank.
Expert Solution
Step 1
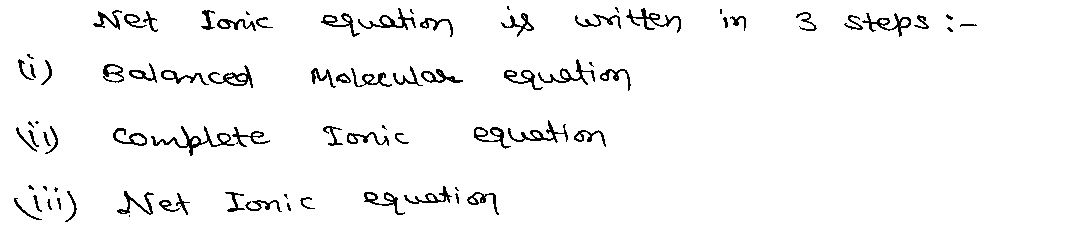
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY