Question 3 refers to the following motion diagram, where the object starts at i and ends at f. The usual convention for motion diagrams applies (time between each dot is the same). In this instance, the distance between the dots is also the same. ino erited lliw slast oft) Hel #3 ● laration of the particle when it is at Bud
Question 3 refers to the following motion diagram, where the object starts at i and ends at f. The usual convention for motion diagrams applies (time between each dot is the same). In this instance, the distance between the dots is also the same. ino erited lliw slast oft) Hel #3 ● laration of the particle when it is at Bud
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
100%
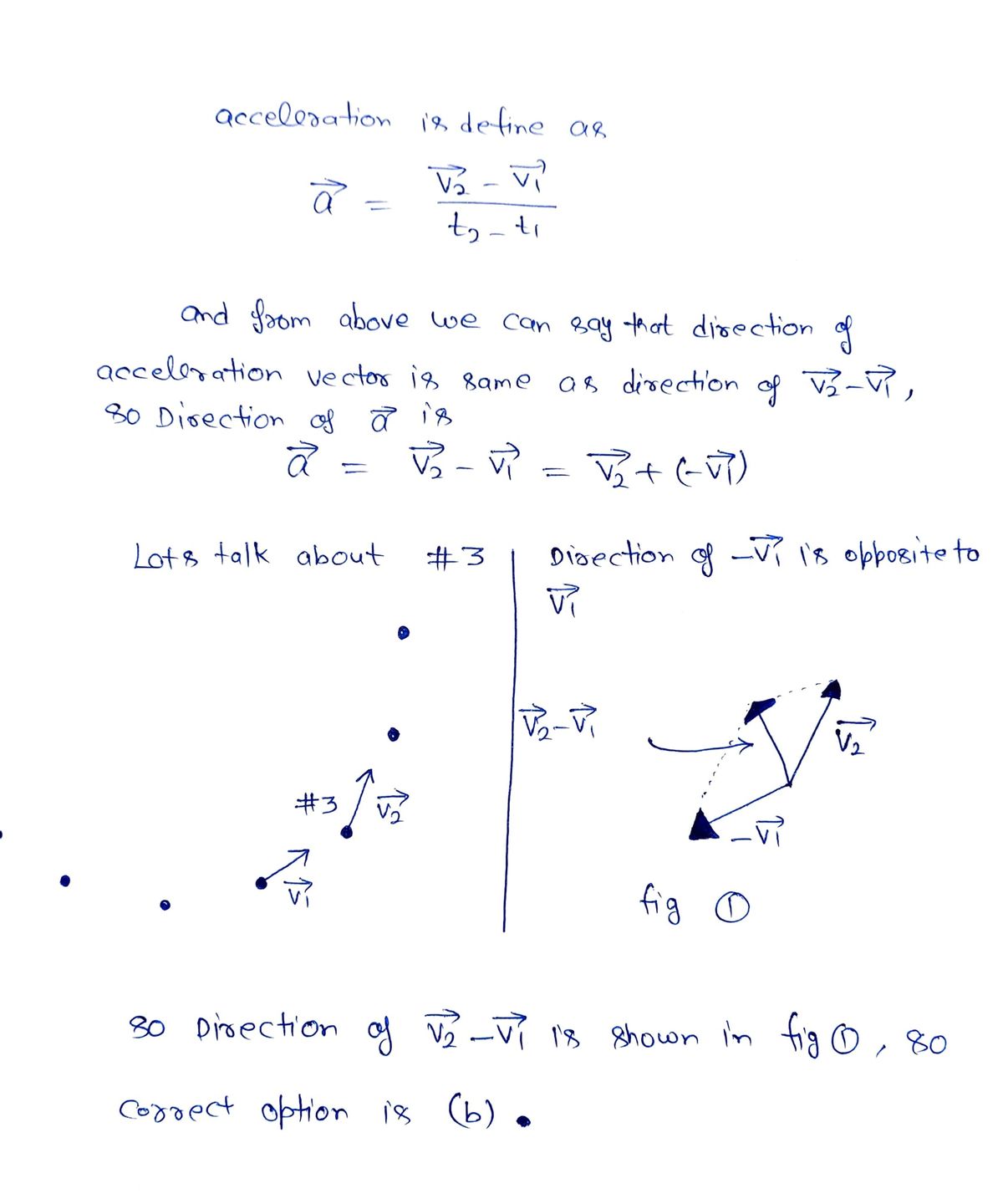
What is the approximate direction of the acceleration of the particle when it is at #3? Do not worry about the magnitude.
The correct answer is B but I am unsure as to why.

Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content on Motion Diagrams**
**Transcript:**
"Question 3 refers to the following motion diagram, where the object starts at i and ends at f. The usual convention for motion diagrams applies (time between each dot is the same). In this instance, the distance between the dots is also the same."
**Diagram Explanation:**
The motion diagram consists of a linear sequence of equally spaced dots indicating the position of an object over consecutive intervals of time.
- **Starting Point (i):** The initial position of the object is marked with the letter 'i'.
- **Ending Point (f):** The final position of the object is marked with the letter 'f'.
- **Intermediate Points (#3):** The object passes through several evenly spaced points, one of which is specifically labeled as '#3'.
The uniform spacing between the dots signifies that the object is moving at a constant speed, as both the time intervals and distances between the points are equal.

Transcribed Image Text:### Transcription for Educational Website
---
This image contains a multiple-choice setup related to vectors and acceleration. Here's the breakdown:
#### Choices:
- **a)** The option is accompanied by an image of a diagonal arrow pointing towards the top right. The choice is circled, indicating it might be the correct or chosen answer.
- **b)** Displays an arrow pointing to the top right.
- **c)** Shows an arrow pointing upwards.
- **d)** Contains the text "The acceleration is 0."
#### Explanation:
- **Graphical Elements:**
- The arrows in options a, b, and c demonstrate vectors typically used in physics to indicate direction and magnitude of forces or velocities.
- Option d states a condition regarding acceleration being zero, indicating a scenario of constant velocity or rest.
Whenever vectors or arrows are discussed, they are typically used to represent directions and magnitudes in vector quantities like velocity or force, critical for understanding motion and dynamics in physics.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON