Question 1 Consider the budget constrained utility maximisation problem between two goods, Good, and Goody. Let x be the quantity of Good, whose price is $13 per unit and y be the quantity of Good, whose price is $15 per unit The total budget is $560. (Therefore, the budget constraint is 13x + 15y = 560). The Utility function is given by U(x, y) = x(y + 1) (a) Solve the problem to maximise the utility, constrained by the budget using Lagrange Multipliers. (b) Show that the solution found does actually maximise the utility function (amongst feasible x and y choices). (c) Calculate the optimal values for x*,y*, λ* and U* (d) Consider now the dual optimisation problem of minimising the cost (Budget, B(x, y)) to achieve the utility U* as calculated in (c). Relate the optimal values of this problem to those found in (c) and also B*.
Question 1 Consider the budget constrained utility maximisation problem between two goods, Good, and Goody. Let x be the quantity of Good, whose price is $13 per unit and y be the quantity of Good, whose price is $15 per unit The total budget is $560. (Therefore, the budget constraint is 13x + 15y = 560). The Utility function is given by U(x, y) = x(y + 1) (a) Solve the problem to maximise the utility, constrained by the budget using Lagrange Multipliers. (b) Show that the solution found does actually maximise the utility function (amongst feasible x and y choices). (c) Calculate the optimal values for x*,y*, λ* and U* (d) Consider now the dual optimisation problem of minimising the cost (Budget, B(x, y)) to achieve the utility U* as calculated in (c). Relate the optimal values of this problem to those found in (c) and also B*.
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
Please provide correct solution and working-out. Greatly Appreciated!!!

Transcribed Image Text:Question 1
Consider the budget constrained utility maximisation problem between two goods,
Good, and Goody.
Let x be the quantity of Good, whose price is $13 per unit and
y be the quantity of Good, whose price is $15 per unit
The total budget is $560. (Therefore, the budget constraint is 13x + 15y
The Utility function is given by U(x, y)
= x(y + 1)
=
560).
(a) Solve the problem to maximise the utility, constrained by the budget using Lagrange
Multipliers.
(b) Show that the solution found does actually maximise the utility function (amongst
feasible x and y choices).
(c) Calculate the optimal values for x*, y*, λ* and U*
(d) Consider now the dual optimisation problem of minimising the cost (Budget, B(x, y))
to achieve the utility U* as calculated in (c). Relate the optimal values of this problem
to those found in (c) and also B*.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Your work-out seems different then mine, Is my work-out correct or yours?
Greatly Appreciated!!

Transcribed Image Text:(a) Solve the problem to maximise the utility, the constraint by the budget using Lagrange multipliers.
Step 1: Initialize the Lagrange function:
L(x, y, ) = (13x + 15y - 560) x(y + 1)
Step 2: Take the partial derivatives and multiply them by zero:
ÔL/ôx = y + 1 - 13λ = 0 (1)
ÔL/ôy = x - 15λ = 0 (2)
13x + 15y - 560 = 0 (3)
Step 3: Concurrently solve the systems of equations (1), (2), and (3):
x = 15λ in equation (2).
When we substitute x in equation (3), we get:
13(15)) + 15y - 560 = 0 195A + 15y - 560 = 0 15y = 560 - 195X (4)
Substituting x = 15 and equation (4) into equation (1)
yields: y + 1 - 13 = 0 y = 13 - 1 (5)
Substituting equation (5) for equation (4):
15(13λ - 1) = 560 - 195X
195A - 15 = 560 - 195A
390A = 575 = 575/390
A = 1.474358974 ≈1.474
Substituting 1.474 into equation (5) yields:
y = 13(1.474) - 1
y = 18.16666667≈ 18.167
Substituting x = 15A into equation (2) yields:
x = 15(1.474)
x = 22.11538462 ≈ 22.11
As a result, the best values are x = 22.11 & y = 18.167.
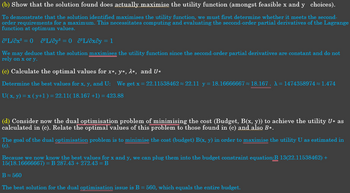
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Show that the solution found does actually maximise the utility function (amongst feasible x and y choices).
To demonstrate that the solution identified maximises the utility function, we must first determine whether it meets the second-
order requirements for a maximum. This necessitates computing and evaluating the second-order partial derivatives of the Lagrange
function at optimum values.
O²L/ox² = 0 O²L/oy² = 0 8²L/əxây = 1
We may deduce that the solution maximises the utility function since the second-order partial derivatives are constant and do not
rely on x or y.
(c) Calculate the optimal values for x*, y*, λ*, and U*
Determine the best values for x, y, and U: We get x = 22.11538462 22.11 y = 18.16666667 ≈ 18.167. A = 1474358974 ≈ 1.474
U( x, y) = x (y+1 ) = 22.11( 18.167 +1) = 423.88
(d) Consider now the dual optimisation problem of minimising the cost (Budget, B(x, y)) to achieve the utility U* as
calculated in (c). Relate the optimal values of this problem to those found in (c) and also B*.
The goal of the dual optimisation problem is to minimise the cost (budget) B(x, y) in order to maximise the utility U as estimated in
(c).
Because we now know the best values for x and y, we can plug them into the budget constraint equation:B 13(22.11538462) +
15(18.16666667) = B 287.43 + 272.43 = B
B≈ 560
The best solution for the dual optimisation issue is B = 560, which equals the entire budget.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education