Q3. a) For the physical system shown in the figure, i. Draw the free-body diagrams of the two masses Ideal pulley M1 X2 M2 K, B ii. Write the equations of motion assuming the system starts from equilibrium. iii. Obtain the Laplace Transform of X2(s)/F(s) equation assuming the external force Fa(s) is applied to mass M1 downward and all initial conditions are zeros.
Transfer function
A transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, subsystem, or component is a mathematical function that modifies the output of a system in each possible input. They are widely used in electronics and control systems.
Convolution Integral
Among all the electrical engineering students, this topic of convolution integral is very confusing. It is a mathematical operation of two functions f and g that produce another third type of function (f * g) , and this expresses how the shape of one is modified with the help of the other one. The process of computing it and the result function is known as convolution. After one is reversed and shifted, it is defined as the integral of the product of two functions. After producing the convolution function, the integral is evaluated for all the values of shift. The convolution integral has some similar features with the cross-correlation. The continuous or discrete variables for real-valued functions differ from cross-correlation (f * g) only by either of the two f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis or not. Therefore, it is a cross-correlation of f(x) and g(-x) or f(-x) and g(x), the cross-correlation operator is the adjoint of the operator of the convolution for complex-valued piecewise functions.

(a)
The free-body diagram of the two rotational systems are drawn below,
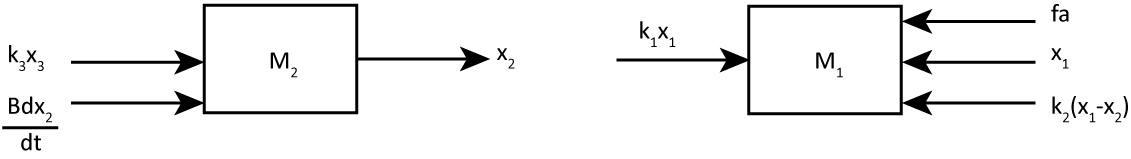
(b)
Differential equations for both the systems at equilibrium is,
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









