Q3) Find the potential u(r, 9) inside a ring 1
Q: What is the electric potential in volts (relative to zero at infinity) at the origin for a charge of…
A:
Q: A thin walled, insulating, hollow cone has a uniform surface charge, and total charge of Q. The…
A: The speed of the electron when it hits the apex of the cone is given by The height of the cone h=5cm…
Q: For the following electric potential: 4(7) = e−3(x-4)+2² Calculate the electric field as a function…
A:
Q: The figure shows a ring of outer radius R = 17.0 cm, inner radius r = 0.260R, and uniform surface…
A:
Q: 1. The potential at the surface of a sphere (radius R) is given by Vo(0) = k cos(46) where k is a…
A: We know that, Surface area of sphere is 4πr² and, Volume of a sphere is (4/3)πr³
Q: Consider a solid sphere of radius R = 0.4 m that is uniformly charged with ρ = -15 μC/m3. What is…
A: Given data: A solid sphere is given. The radius of the sphere is, R= 0.4 m The volume charge density…
Q: The electric potential in a region of space is given by: V(x, y, z) = (2.5 V/m²) xy² + (1.5 V/m²)…
A: To find the electric field from the given potential function, we need to take the gradient of the…
Q: what is the electric potential in volts (relative to zero at infinity) at the origin for a charge of…
A: Given: Charge density (λ) = 14.48 nC/m. Electric field zone (z1) = 2.9 m. to (z2) = 5.58 m.
Q: A rod of length L lies along the x axis with its left end at the origin. B It has a non-uniform…
A:
Q: (a) Find the electric potential, taking zero at infinity, at the upper right corner (the corner…
A:
Q: An ideal electric point dipole is a theoretical construction involving two point electric charges e…
A: Consider the following diagram:
Q: a volume V in vacuum is boundary by a surface S consisting of several separate conducting surfaces…
A: a) To show that the capacitance of one conductance, b) To show that true capacitance C is always…
Q: A thin, spherical, conducting shell of radius R is mounted on an isolating support and charged to a…
A: We use the law of conservation of energy (1/2)mv2 = qV v=2qVm V=-715 V magnitude of V=715…
Q: The figure shows a ring of outer radius R = 10.0 cm, inner radius r = 0.180R, and uniform surface…
A: Given a ring of outer radius R = 10.0 cm=.1m, inner radius r = 0.180R, and uniform surface charge…
Q: A thin glass rod of length 2L has a linear charge density that is zero in the middle of the length…
A: Solution attached in the photo. There is a correction in question in the expression of given…
Q: Consider a uniformly volume-charged sphere of radius R and charge Q. What is the electric potential…
A: The charge on the sphere is Q .The radius of the sphere is R
Q: A finite linear charge distribution has a total charge Q and length l. The linear charge density is…
A:
Q: A rod of length L = 0.55 m is placed along the x-axis with its center at the origin. The rod has a…
A: The electric potential at a point due to a point charge q at a distance r is given by:,Where is…
Q: A conducting sphere of radius 'a' has a constant electric potential at its surface equal to V(a,0) =…
A:
Q: A rod sits horizontally along the x-axis with a continuous uniform charge distribution such that the…
A:
Q: An electron is at the origin. (a) Calculate the electric potential VA at point A, x = 0.250 cm. (b)…
A: Given,
Q: -5- n region -10- www -- --
A: The potential on plate c is 10 volt according to diagram 1 magnitude of electric field in region 2…
Q: A rod of length L = 4.00 m with uniform charge of 6.80 nC/m is oriented along the y axis as shown in…
A: Formula of electric potential at axial point of uniformly charged rod is as follow: V=kλlnd+Ld…
Q: Find the electric potential at a distance r > R from the center of the sphere, assuming that the…
A: Given: The distance for electric potential is r > R. The potential at large distances from the…
Q: Set up, but do not evaluate, an integral for the electric potential a distance R from the centre of…
A:
Q: Consider a spherical thin shell of radius R with charges uniformly distributed on its surface. The…
A: Given the charge density of thin spherical shell, σr=σ the radius of the thin spherical shell is, r…
Q: A sphere of radius a has potential (sin 2θ)( cos ϕ) on its surface. Find the potential at all points…
A: To find the potential at points outside the sphere, we can use the concept of multipole expansion.…

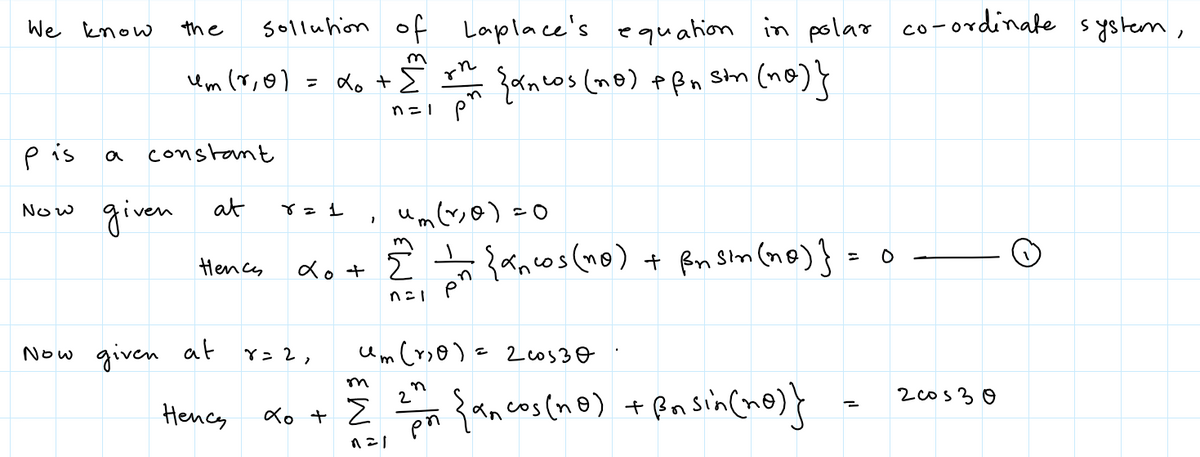
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- Suppose we have an electric potential that is a function of z and the distance in the transverse plane, Vx2 + y?. In other words, o → ¢(rl,z). Show that the gradient can be written V¢ = dz Similarly, suppose we have a potential that is purely a function of the distance, r = from the origin. Show that the gradient can be written Vx2 + y2 + z², Vø = arAn isolated conducting sphere of radius r1 = 0.20 m is at a potential of -2000V, with charge Qo. The charged sphere is then surrounded by an uncharged conducting sphere of inner radius r2 = 0.40 m, and outer radius r3 = 0.50m, creating a spherical capacitor. (a)Draw a clear physics diagram of the problem. (b) Determine the charge Qo on the sphere while its isolated. (c)A wire is connected from the outer sphere to ground, and then removed. Determine the magnitude of the electric field in the following regions: R<r1 ; re<R < r2; r2< R < r3; r3 < R (d) Determine the magnitude of the potential difference between the sphere and the conducting shell. (e) Determine the capacitance of the spherical capacitor.What is the electric potential in volts (realative to zero at infinity) at the origin for a charge of uniform density 14.62 nC/m is distributed along the z axis from z=2,5 m to z=5.78 m Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
- SSD_W06_04 0/3 points (graded) R. +Q B R. The figure above shows a solid insulating sphere of radius R2 with charge -Q (Q > 0) distributed uniformly throughout the volume. This sphere is centered within a thin spherical shell of radius R1; a charge +Q is distributed uniformly on the surface of the spherical shell. Very far away from the sphere and the spherical shell, the electric potential is zero. Use k for Coulomb's constant. At point A on the surface of the spherical shell, what is the electric potential VA? VA = Point B is on the surface of the sphere. What is the potential difference, VB – VẠ? VB - VA = Point C is at the center of the sphere. What is the potential difference, Vo - VB? Ve - VB =E1.3Consider a solid insulating sphere which has a total chargeof +3Q but is distributed as ρ(r) = βr, and has a radius of a. This issurrounded by a conducting shell that has a charge of −3Q placed onits outer surface. The inner radius is b and the outer radius is c. a) Determine β in terms of Q and a.b) Find the potential at all points in space
- A thin rod extends along the x-axis from x = −a to x = a . The rod carries a positive charge +Q uniformly distributed along its length 2a with charge density λ, as shown in Figure attached. a) Use dV = 1/4πε0 ∫ dq/r to show that the electric potential at point P is given by: V(x) = (λ/4πε0) ln(x + a/x − a) b) What is the electric potential of the rod at x = 4a and x = 2a? c) What is the electric potential difference between x = 4a and x = 2a?What is the electric potential in volts (relative to zero at infinity) at the origin for a charge of uniform density 13.97 nC/m is distributed along the z axis from z = 2.1 m to z = 6.45 m. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.What is the electric potential in volts (relative to zero at infinity) at the origin for a charge of uniform density 11.46 nC/m is distributed along the z axis from z = 2.6 m to z = 6.12 m.
- A cylindrical shell of radius R, and height his charged with charge that is uniformly distributed over it surface. To find the electric potential due to this shell at point Pa distance d from its right base we take, as an element, a thin ring that has a charge element: ut of dx Select one: O dq = o(2 TRdx) O dq = o(2 Trdr) O dq = p(TR?dx) dq = o(TR?dx) Two concentric conducting spherical shells of radii a and bare charged to a total charge Q. If the two shells are connected as shown. Which of the following is false? en 5 ete D out of REDMI NOTE 9 144 AI QUAD CAMERAWhen an uncharged conducting sphere of radius a is placed at the origin of an xyz coordinate system that lies in an initially uniform electric fieldE = E, k, the resulting electric potential is V (x,y,z) = Vo for the points inside the sphere and V (x,y,z) = Vo – Egz + Ega³z (x² + y² + z²)3/2 for points outside the sphere, where V is the (constant) electric potential on the conductor. Use this equation to determine the x, y, and z components of the resulting electric field in the following regions. (Use the following as necessary: X, y, z, a, and Eo:)The electric potential in a region of space varies as V=by/(a2+y2)V=by/(a2+y2). Determine the components of E→ Express your answers in terms of the variables a, b, and y separated by commas..