Consider the following short descriptions. Indicate whether each description more closely relates to a major feature of financial accounting (use FA) or management accounting (use MA) a. Behavioral impact is secondary b. Is constrained by generally accepted accounting principles C. Has a future orientation d. Is characterized by detailed reports e. Field is more sharply defined f. Has less flexibility on
Consider the following short descriptions. Indicate whether each description more closely relates to a major feature of financial accounting (use FA) or management accounting (use MA) a. Behavioral impact is secondary b. Is constrained by generally accepted accounting principles C. Has a future orientation d. Is characterized by detailed reports e. Field is more sharply defined f. Has less flexibility on
Chapter1: Financial Statements And Business Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1Q
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1.2
Consider the following short descriptions. Indicate whether each description more
closely relates to a major feature of financial accounting (use FA) or management accounting
(use MA)
a. Behavioral impact is secondary
b. Is constrained by generally accepted accounting principles
C. Has a future orientation
d. Is characterized by detailed reports
e. Field is more sharply defined
f. Has less flexibility
On
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
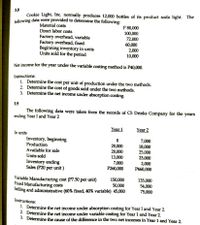
Transcribed Image Text:3.8
Cookie Light, Inc. normally produces 12,000 bottles of its product soda light. The
following data were provided to determine the following:
Material costs
Direct labor costs
P 80,000
Factory overhead, variable
Factory overhead, fixed
Beginning inventory in units
Units sold for the period
100,000
72,000
60,000
2,000
10,000
Net income for the year under the variable costing method is P40,000.
Instructions:
1. Determine the cost per unit of production under the two methods.
2. Determine the cost of goods sold under the two methods.
3. Determine the net income under absorption costing.
3.9
The following data were taken from the records of C5 Drinks Company for the years
ending Year I and Year 2
Year 1
Year 2
In units
Inventory, beginning
Production
Available for sale
Units sold
20,000
20,000
13,000
7,000
P260,000
7,000
18,000
25,000
23,000
2,000
P460,000
Inventory ending
Sales (P20 per unit )
Variable Manufacturing cost (P7.50 per unit)
Fixed Manufacturing costs
Selling and administrative (60% fixed, 40% variable) 45,000
150,000
50,000
135,000
54,000
75,000
Instructions:
1. Determine the net income under absorption costing for Year I and Year 2.
2. Determine the net income under variable costing for Year 1 and Year 2.
3. Determine the cause of the difference in the two net incomes in Year 1 and Year 2.
Solution
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:22
An organization has the following total costs at two activity levels
P150,000 @ 16,000 units;
P200,000 @ 24,000 units
Variable costs per unit is constant in this range of activity and there is a step down of
P20,000 in the total fixed costs when activity is below 18,000 units.
1. What is the total cost at an activity level of 17,000 units?
2 What is the total cost at an activity level of 25,000 units?
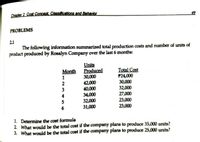
Transcribed Image Text:Chepter 2 Cost Concent. Classifications and Behavior
49
PROBLEMS
21
The following information summarized total production costs and number of units of
product produced by Rosalyn Company over the last 6 months:
Units
Produced
30,000
42,000
40,000
34,000
32,000
31,000
Total Cost
P24,000
30,000
32,000
27,000
23,000
23,000
Month
4
1. Determine the cost formula
2. What would be the total cost if the company plans to produce 35,000 units?
3. What would be the total cost if the company plans to produce 25,000 units?
123 56
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272094
Author:
WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619202
Author:
Hall, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272094
Author:
WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619202
Author:
Hall, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis…
Accounting
ISBN:
9780134475585
Author:
Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781259722660
Author:
J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781259726705
Author:
John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education