Problem 6: If cable AB is subject to a tension of 700 N, determine the tension in cables AC and AD and the magnitude of the vertical force F. 3m 6 m 6 m -3m- B 2m 1.5 m
Q: The mass of the cylinder is 50 kg. 0 = 65 degrees B 0 C Ө The tension in the cable AC is most…
A: We will first identify the forces in the system and resolve them into horizontal and vertical…
Q: 14 chapter30-question16 In Figure, assume 4 = 2.00 A and I, = 6.00 A. What is the relationship…
A: c)Option 3
Q: Consider the same situation as in the previous problem. This time the magnet has mass 6.08 kg and…
A:
Q: 14.32 Label the directions and mark the po- larities for the six unique currents in the cir- cuit…
A: IT = 1.169 AI1 = 0.915 AI2 = 0.254 AI3 = 0.315 AI4 = 0.6 AI5 = 0.569 AExplanation:
Q: How do you use this physics discovery in your everyday life in regards to Coulombs Law? Could you…
A: While blow-drying your hair, you notice certain strands standing on end, particularly near the dryer…
Q: 1. Problem No. 1: A series of cables are connected to a ring at B and D, as shown in the figure. For…
A:
Q: The field inside a solenoid is given by B=µn I. Explain what each quantity is in this formula.
A:
Q: The values for the components of the circuit shown in the figure are V = 15 V, C = 3.5 μF, and L =…
A:
Q: A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic…
A: Using Newton's law, Ffr=FBμsmg=BILμs=BILmg=BVLmgR Since, I=VR
Q: Verify, as was concluded without proof , that units of T ⋅ m2 / A = Ω ⋅ s = H .
A: Starting from the unit Henry,
Q: a) 1/R=1/R1+1/R2 R1=60Ω R2=40Ω 1/60Ω+1/40 Ω= 2+3/120 Ω So R=1/24 Ω What's wrong with this?…
A: Part A. R1=60 ohm, R2=40 ohm Therefore, 1R=1R1+1R21R=160+1401R=5120R=24 ohm Hence, correct value of…
Q: The two wires shown in the figure below are separated by d = 11.0 cm and carry currents of I= 4.95 A…
A: To find the magnetic field at different points due to the currents in the wires, we can use the…
Q: = For the circuit shown below, € = 18.7V, R₁ = 44.2 Ohms, R₂ 20.6Ohms, and L= 40.4 H. S₁ remains…
A:
Q: In the circuit shown below, switch S2 is open and switch S1 is closed until inductor L1 is charged…
A: The objective of the question is to find the current through the inductor L1 when switch S2 is…
Q: Same situation as in the previous two problems this time the magnet s mass is 4.00 kg and the…
A:
Q: EMF (Volts) time (milliseconds - Part A What is the anmplitude of this EMF? Eg =
A:
Q: A 3.1 g aluminum foil ball with a charge of +4.6x10-9 C is suspended on a string in a uniform…
A:
Q: Calculate I₂.
A:
Q: C3 C4 C1 C2
A: A network of capacitances
Q: 1. 2 12 t(s) Determine the time constant of the LR circuit. TH If L = 6 H, determine R. R = P
A: By observing the graph; The maximum current Imax=3.8A As we know that the current in delay is equal…

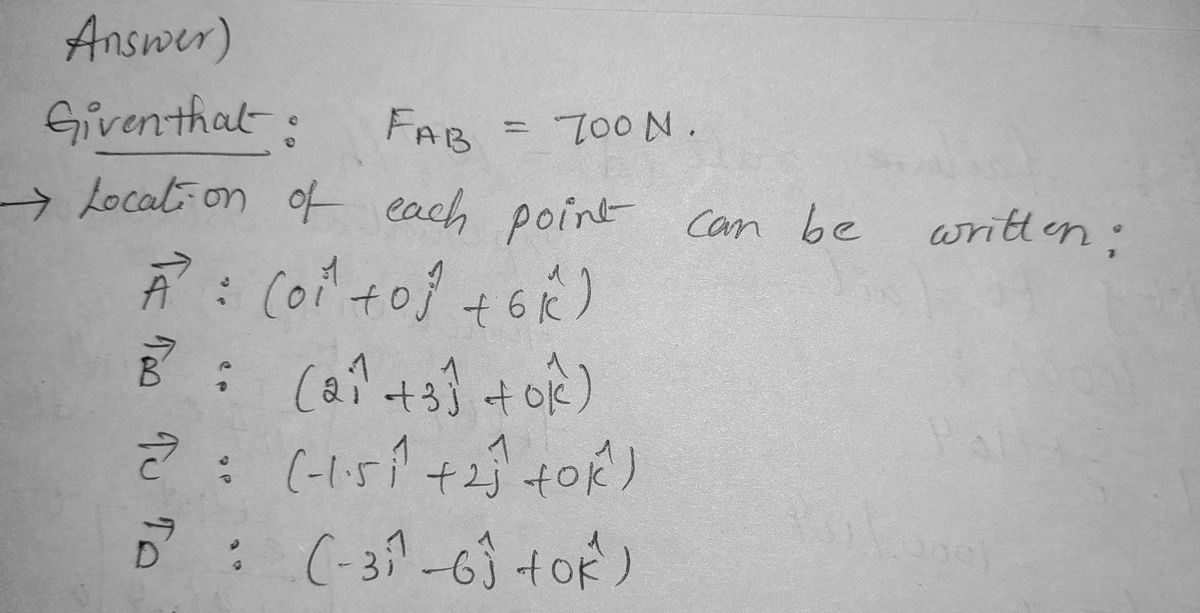
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

- I 3 a ↑ R1 $220 R2 330 R3 390 I2 I3 vi 12V A * В Calculations: Node Equα tion: Σ I i-ΣΙ out 11 + 12 = 13 Loop Equation: Loop 1: – 11(R1) + 12(R2) – V1 = 0 Loop 2:What is the net force (magnitude and direction) on each wire in the figure Below, in which I = 12 A? I wire 1 wire 2 wire 3 I 2 1 50 cm N |--Direction-- ✓ N |--Direction-- ✓ N --Direction-- ✓ 2 cm 2 cmThe transformer on a model train set steps down the voltage from 120 Volts to 9.0 Volts. The number of turns on the secondary coil is 30. The train draws 6.0 A of current on the secondary coil. What is the current draw on the primary coil? 0.45 A 180 A 80 A 13.5 A
- What is the value of R3? R1 = 14.0 Ω, R2 = 10.0 Ω, ΔV = 9.00 V and I = 308 mA. 5.83 Ω 23.4 Ω 5.22 Ω 29.2 ΩSelect all of the following descriptions that match what happens when a ferromagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field. 1) The ferromagnetic material becomes negatively charged. 2) Nothing, ferromagnetic materials do not interact with magnetic fields. 3)The ferromagnetic material rapidly cools. 4)The ferromagnetic material becomes positively charged. 5)The external magnetic field induces magnetic poles in the ferromagnetic material. 6)The ferromagnetic material becomes magnetized.11. * Marco has decided to build an electromagnet for his children to use as a toy to lift up their matchbox cars like a real crane might. He takes an ordinary iron nail and wraps some copper wire around it 20 times. When he connects this to a small battery he discovers that although the electromagnet turns on and sticks to the car, it is not strong enough to lift it securely into the air. Explain three ways in which he could improve the strength of his electromagnet and justify which of these three methods you would suggest he uses.