Problem 2: When a particular rubber ball is dropped from a given height (in meters), its impact speed (in meters/second) when it hits the ground is given by the formula: speed S = /2gh %3D where g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height. The ball then rebounds to 2/3 the height from which it last fell. Using the formula, design, write and run a C++ program that will accept input values from the user at run time and display the impact speed of the first three bounces and the rebound height of each bounce. Test your program using an initial height of 18 m. Run your program twice, and compare the results for dropping the ball on Earth (g 9.81 m/s²) and on the Moon (g = 1.67 m/s2). [Hint: In Step 2: Design a solution, use a Table to organize the solution before going to Step 3: Coding] Save this program as Module3Proj2.
![Problem 2: When a particular rubber ball is dropped from a given height (in meters), its
impact speed (in meters/second) when it hits the ground is given by the formula:
speed S = /2gh
%3D
where g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height. The ball then rebounds to
2/3 the height from which it last fell. Using the formula, design, write and run a C++
program that will accept input values from the user at run time and display the impact
speed of the first three bounces and the rebound height of each bounce. Test your
program using an initial height of 18 m. Run your program twice, and compare the
results for dropping the ball on Earth (g = 9.81 m/s?) and on the Moon (g = 1.67 m/s2).
[Hint: In Step 2: Design a solution, use a Table to organize the solution before going to
Step 3: Coding]
Save this program as Module3Proj2.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fc2affbda-d1ca-40f2-8c86-f29db5c7e1f4%2Fe5c84704-a1ef-495e-86f5-692ed4eb5a60%2Fuyo7ufd_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Algorithm:
step1: take height and g value from user(for both moon and earth case separately)
step2:declare and initializes required variables;
step3: calculate speed as speed=sqrt(2*g*h)
step4: update height for each bounce
step5: update values of i(denote for each bounce)
step6: stop
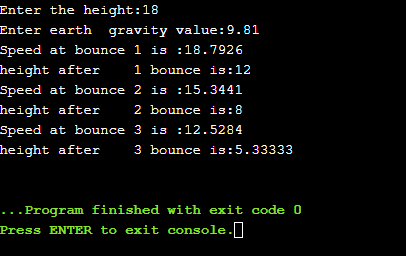
# Source_code
#include <iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float intial_height,speed;
float g;
int i=1;
cout<<"Enter the height:";
cin>>intial_height;
cout<<"Enter earth gravity value:";
cin>>g;
while(i<=3){
speed=sqrt(2*g*intial_height);
cout<<"Speed at bounce\t"<<i<<" is :"<<speed<<endl;
intial_height=(intial_height*2)/3;
cout<<"height after\t"<<i<<" bounce is:"<<intial_height<<endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









