Problem 1: A problem of practical interest is to make a beam of elec- trons turn a 90° corner. This can be done with the parallel-plate capac- itor shown in Fig. 1. An electron with kinetic energy Ekin = 3.0 × 10-17 J enters through a small hole in the bottom plate of the capacitor. What strength electric field is needed if the electron is to emerge from an exit hole l=1.0 cm away from the entrance hole, traveling at right angle to its original direction? For which distance d between the plates this is possible? (Answer: E= 3.75 x 10¹ N/C.)
Problem 1: A problem of practical interest is to make a beam of elec- trons turn a 90° corner. This can be done with the parallel-plate capac- itor shown in Fig. 1. An electron with kinetic energy Ekin = 3.0 × 10-17 J enters through a small hole in the bottom plate of the capacitor. What strength electric field is needed if the electron is to emerge from an exit hole l=1.0 cm away from the entrance hole, traveling at right angle to its original direction? For which distance d between the plates this is possible? (Answer: E= 3.75 x 10¹ N/C.)
Related questions
Question
I need help with problems A,B,C,D and E. I am really struggling with this problem I asked my professor and he won't help me. I was wondering if you can help me solve these problems. Also, Can you label which problem is A,B,C,D and E. Thank you

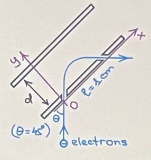
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1: A problem of practical interest is to make a beam of elec-
trons turn a 90° corner. This can be done with the parallel-plate capac-
itor shown in Fig.1. An electron with kinetic energy Ekin = 3.0 × 10-¹7 J
enters through a small hole in the bottom plate of the capacitor. What
strength electric field is needed if the electron is to emerge from an exit
hole l = 1.0 cm away from the entrance hole, traveling at right angle to
its original direction? For which distance d between the plates this is
possible? (Answer: E = 3.75 x 10¹ N/C.)
a) Which plate of the capacitor should be positive and which one
should be negative if you want the electron to turn to the right? In
Fig.1, draw the electric field created by the plates.
(0=45)
10 l=10m
electrons
FIG. 1: The scheme for Problem 1
b) Pick the coordinate system xy as shown in Fig.1. From the kinetic energy of the electron, compute
the magnitude of its velocity, oo, when it enters the capacitor, as well as its coordinate components, vox and
Doy. Do not plug any numerical values into the formulae at this step. Work only with symbols and coefficients.
Express the coordinate components of electron's acceleration, ax and ay, in terms of the electric field
between the plates. Note that one of the components must be negative (which one?).
c) The electron moves between the plates along a ballistic trajectory (analogous to the trajectory of a
projectile moving in the gravitational field of the Earth). The coordinates as functions of time are given by
the following expressions that should be familiar from mechanics: x = xo +Voxt + x², y = yo +Voyt + y²
From the requirement that the electron returns to the position y = 0 after passing 1 cm in x direction,
deduce the acceleration of the electron, and from there the electric field strength needed to produce this
acceleration. Work only with symbols until you get the final formula for E, expressed in terms of Ekin, e,
I and 0.¹

Transcribed Image Text:d) Now plug in the numbers into the formula for Ey to compute its value.
e) Note that there is a minimum separation dmin that the plates must have for the trajectory to fit
between them. Working with symbols only, show that if 0 = 45° the minimum separation is dmin -
(there is even no need to use a calculator to compute it).
=
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images
