Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Pls explain chair conformations

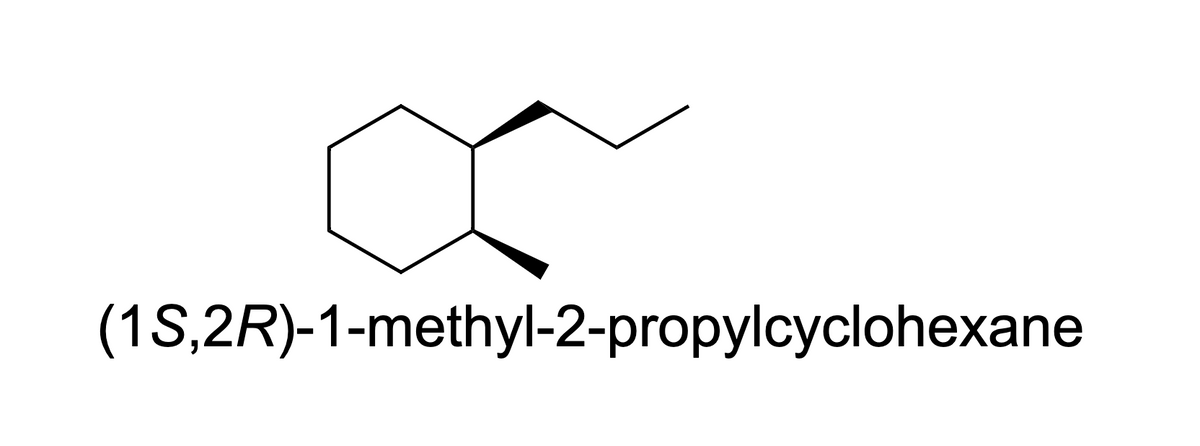
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Drawing the Most Stable Chair Conformation for a Cyclohexane Derivative**
**Objective:**
Learn how to draw the most stable chair conformation for a given cyclohexane compound.
**Task:**
Draw the most stable chair conformation for the compound shown.
**Compound Description:**
- The compound depicted is a cyclohexane ring with two substituents.
- The substituents are located on adjacent carbon atoms.
- The first substituent is an ethyl group (two carbon chain) located on the top right carbon.
- The second substituent is a methyl group (single carbon) located on the bottom right carbon, represented in a wedge, indicating it is above the plane of the ring.
**Tips for Drawing the Chair Conformation:**
1. **Identify the Axial and Equatorial Positions:**
- In a chair conformation, each carbon has one axial and one equatorial bond.
- Larger groups should be placed in equatorial positions to minimize steric strain.
2. **Place Larger Substituents Equatorially:**
- Given the size of ethyl and methyl groups, ethyl is the larger group and should be placed equatorially if possible.
3. **Consider Stereochemistry:**
- Ensure that the orientation (upward or downward) of the substituents matches the original compound configuration.
4. **Sketching the Chair:**
- Draw a zig-zag line to represent the cyclohexane ring.
- Add substituents appropriately, considering steric hindrance and stability.
**Conclusion:**
By placing the larger substituents in equatorial positions and maintaining the stereochemistry, you can draw the most stable chair conformation for this cyclohexane derivative. This minimizes potential steric strain and leads to a lower energy, more stable structure.
Expert Solution
Step 1
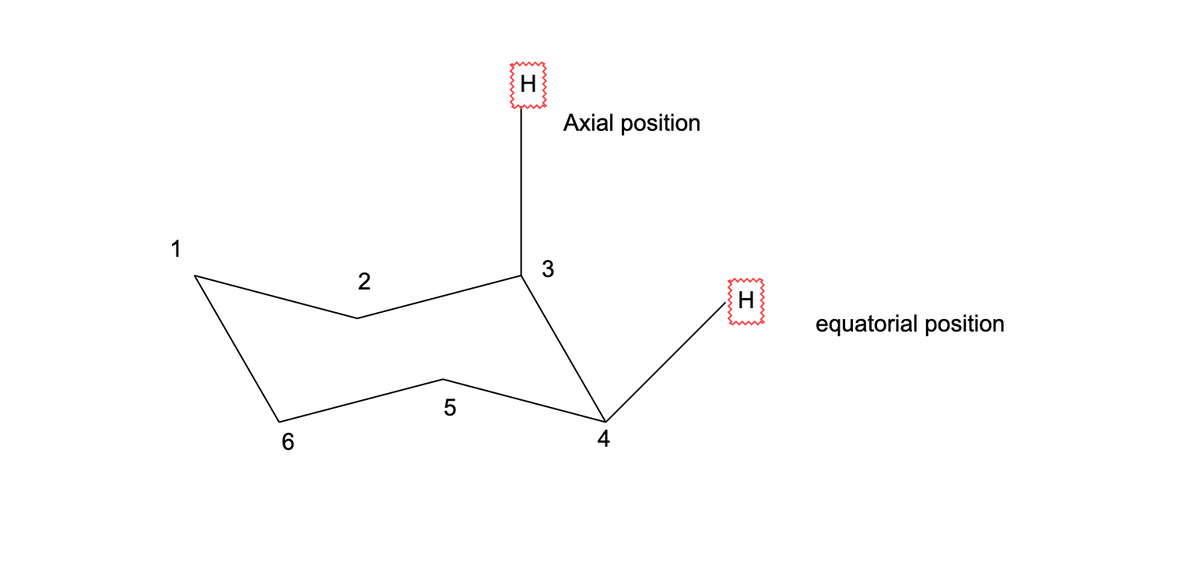
Chair conformation: Chair conformation consists of two planes:
carbon 1,3 and 5 - in one plane
carbon 2,4,and 6 - in another plane
chair conformation have two positions - one is axial and another is equatorial.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY