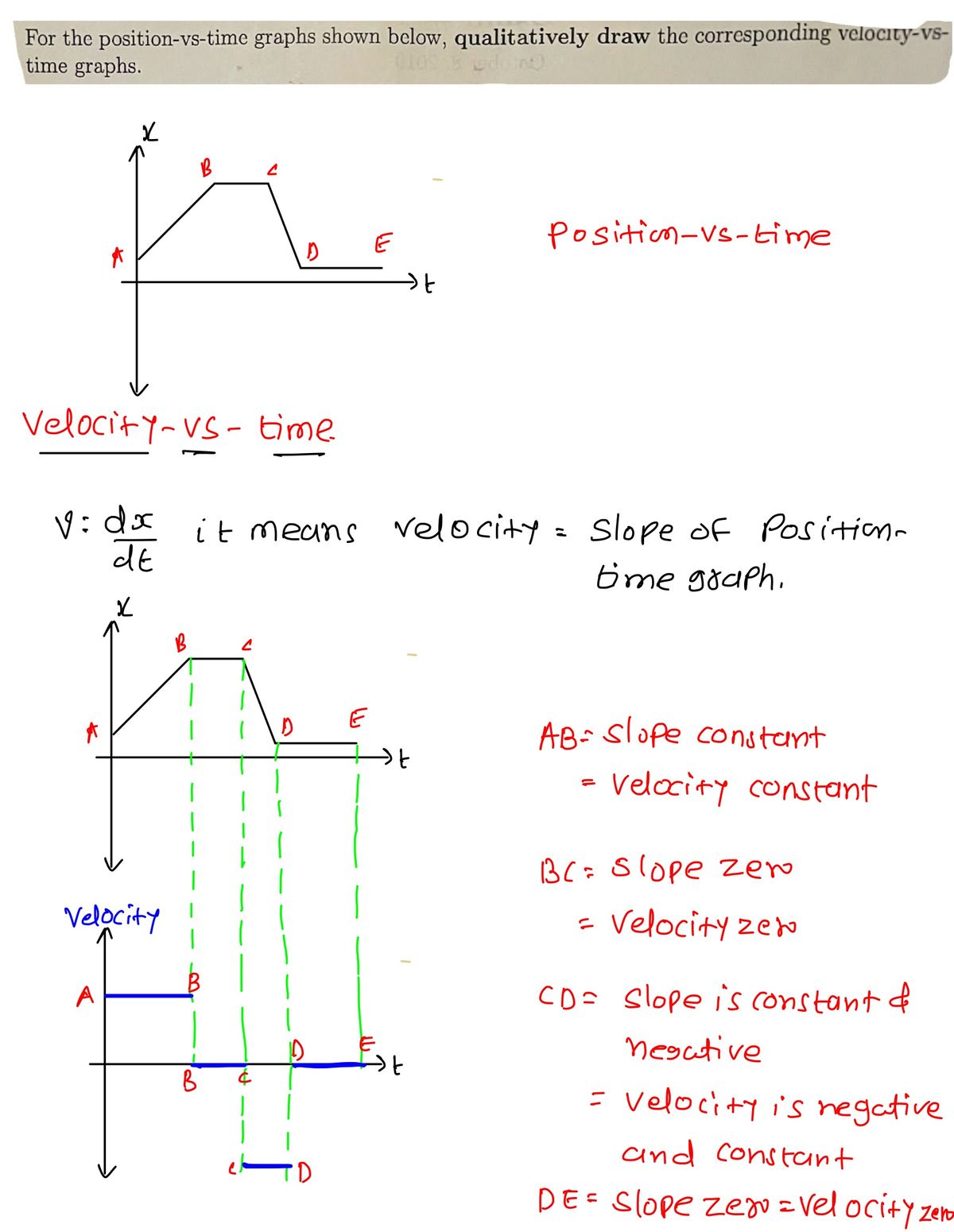
For the position-vs-time graphs shown below, qualitatively draw the corresponding velocity-vs-time graphs. ### Graph Analysis: #### Left Graph: - **Position-vs-Time Graph**: - The graph starts at the origin and quickly rises to a peak. - After reaching the peak, it descends at the same slope and becomes flat again. - **Velocity-vs-Time Graph**: - The initial horizontal segment indicates a constant, positive velocity. - As the line rises toward the peak, there is a steep positive slope, indicating increased speed. - The descent shows a steep negative slope, indicating a decrease in speed. - The flat section at the end indicates a return to constant velocity. - **Notes**: - There is a note pointing to the flat section saying "more negative?" suggesting further analysis. #### Right Graph: - **Position-vs-Time Graph**: - The graph starts high on the vertical axis and initially descends steeply. - The slope becomes less steep as it flattens out over time. - **Velocity-vs-Time Graph**: - The graph indicates a steady negative velocity, then approaches zero as the position graph flattens. - This indicates a decreasing speed as the slope of the position graph lessens. - **Notes**: - There is a note pointing to the decreasing slope stating "slope" indicating analysis of the changing rate of the position. Both diagrams are used to understand the relationship between position, velocity, and time. The velocity-vs-time graph is derived by examining the slopes of the corresponding position-vs-time graph.
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
In classical mechanics, kinematics deals with the motion of a particle. It deals only with the position, velocity, acceleration, and displacement of a particle. It has no concern about the source of motion.
Linear Displacement
The term "displacement" refers to when something shifts away from its original "location," and "linear" refers to a straight line. As a result, “Linear Displacement” can be described as the movement of an object in a straight line along a single axis, for example, from side to side or up and down. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Linear displacement is usually measured in millimeters or inches and may be positive or negative.

-
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









