Part II: Determine the type of inheritance: For each of the following examples, determine the most likely form of inheritance. These may be any type of inheritance we have discussed so far this semester. It may be impossible to determine with 100% certainty what the inheritance form is based on the information you have here, but you should use the information provided to make an educated prediction. Then, give a brief explanation to justify your selection including evidence or work you performed, such as Punnett squares or genotypes of parents or offspring, for all questions. 1. In one cross, a female flower that produces large anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces small anthers. All offspring produce large anthers. In a second cross, a female flower that produces small anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces large anthers. All offspring produce small anthers.
Part II: Determine the type of inheritance: For each of the following examples, determine the most likely form of inheritance. These may be any type of inheritance we have discussed so far this semester. It may be impossible to determine with 100% certainty what the inheritance form is based on the information you have here, but you should use the information provided to make an educated prediction. Then, give a brief explanation to justify your selection including evidence or work you performed, such as Punnett squares or genotypes of parents or offspring, for all questions. 1. In one cross, a female flower that produces large anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces small anthers. All offspring produce large anthers. In a second cross, a female flower that produces small anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces large anthers. All offspring produce small anthers.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
#1 please

Transcribed Image Text:**Part II: Determine the type of inheritance**
For each of the following examples, determine the most likely form of inheritance. These may be any type of inheritance we have discussed so far this semester. It may be impossible to determine with 100% certainty what the inheritance form is based on the information you have here, but you should use the information provided to make an educated prediction. Then, give a brief explanation to justify your selection, including evidence or work you performed, such as Punnett squares or genotypes of parents or offspring, for all questions.
1. In one cross, a female flower that produces large anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces small anthers. All offspring produce large anthers. In a second cross, a female flower that produces small anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces large anthers. All offspring produce small anthers.
2. A zebra weighing 78 kg was crossed with a zebra weighing 55 kg, and the offspring produced was 62 kg. When the 62 kg offspring was crossed with a zebra weighing 70 kg, the new offspring produced was 68 kg.
3. A tan-colored female mouse is crossed with a white-colored male mouse. All of the male offspring produced from this cross were tan, while all of the female offspring produced by this cross had patches of tan and white coloration.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
#2 please
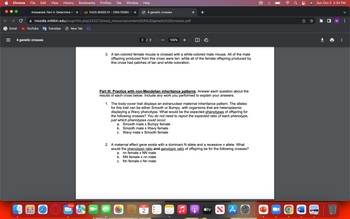
Transcribed Image Text:**Part III: Practice with non-Mendelian inheritance patterns**
Answer each question about the results of each cross below. Include any work you performed to explain your answers.
1. The body-cover trait displays an extranuclear maternal inheritance pattern. The alleles for this trait can be either Smooth or Bumpy, with organisms that are heteroplasmic displaying a Wavy phenotype. What would be the expected phenotypes of offspring for the following crosses? *You do not need to report the expected ratio of each phenotype, just which phenotypes could occur.*
a. Smooth male x Bumpy female
b. Smooth male x Wavy female
c. Wavy male x Smooth female
2. A maternal effect gene exists with a dominant N allele and a recessive n allele. What would the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of offspring be for the following crosses?
a. nn female x NN male
b. NN female x nn male
c. Nn female x Nn male
Solution
Follow-up Question
#1 please
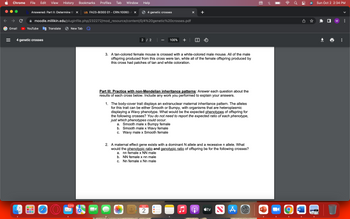
Transcribed Image Text:**Part III: Practice with Non-Mendelian Inheritance Patterns**
Answer each question about the results of each cross below. Include any work you performed to explain your answers.
1. **The body-cover trait displays an extranuclear maternal inheritance pattern.** The alleles for this trait can be either Smooth or Bumpy, with organisms that are heteroplasmic displaying a Wavy phenotype. What would be the expected **phenotypes** of offspring for the following crosses? You do not need to report the expected ratio of each phenotype, just which phenotypes could occur.
a. Smooth male x Bumpy female
b. Smooth male x Wavy female
c. Wavy male x Smooth female
2. **A maternal effect gene exists with a dominant N allele and a recessive n allele.** What would the **phenotypic ratio** and **genotypic ratio** of offspring be for the following crosses?
a. nn female x NN male
b. NN female x nn male
c. Nn female x Nn male
Solution
Follow-up Question
#3 please
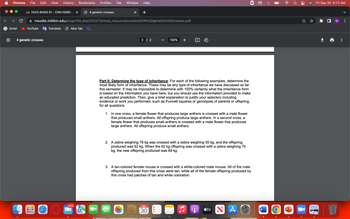
Transcribed Image Text:**Part II: Determine the Type of Inheritance**
For each of the following examples, determine the most likely form of inheritance. These may be any type of inheritance we have discussed so far this semester. It may be impossible to determine with 100% certainty what the inheritance form is based on the information you have here, but you should use the information provided to make an educated prediction. Then, give a brief explanation to justify your selection including evidence or work you performed, such as Punnett squares or genotypes of parents or offspring, for all questions.
1. **Example 1: Flower Cross**
- In one cross, a female flower that produces large anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces small anthers. All offspring produce large anthers. In a second cross, a female flower that produces small anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces large anthers. All offspring produce small anthers.
2. **Example 2: Zebra Cross**
- A zebra weighing 78 kg was crossed with a zebra weighing 55 kg, and the offspring produced was 62 kg. When the 62 kg offspring was crossed with a zebra weighing 70 kg, the new offspring produced was 68 kg.
3. **Example 3: Mouse Color Cross**
- A tan-colored female mouse is crossed with a white-colored male mouse. All of the male offspring produced from this cross were tan, while all of the female offspring produced by this cross had patches of tan and white coloration.
Solution
Follow-up Question
#2 please
Transcribed Image Text:Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
Gmail
с
in FA23-B1300 01 - CRN:10060: A X
YouTube
4 genetic crosses
moodle.millikin.edu/pluginfile.php/232272/mod_resource/content/0/4%20genetic%20crosses.pdf
Translate
O
New Tab
4 genetic crosses
9,310
X
+
2 / 2
100% +
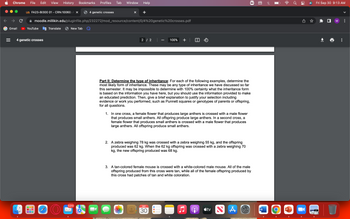
Part II: Determine the type of inheritance: For each of the following examples, determine the
most likely form of inheritance. These may be any type of inheritance we have discussed so far
this semester. It may be impossible to determine with 100% certainty what the inheritance form
is based on the information you have here, but you should use the information provided to make
an educated prediction. Then, give a brief explanation to justify your selection including
evidence or work you performed, such as Punnett squares or genotypes of parents or offspring,
for all questions.
1. In one cross, a female flower that produces large anthers is crossed with a male flower
that produces small anthers. All offspring produce large anthers. In a second cross, a
female flower that produces small anthers is crossed with a male flower that produces
large anthers. All offspring produce small anthers.
2. A zebra weighing 78 kg was crossed with a zebra weighing 55 kg, and the offspring
produced was 62 kg. When the 62 kg offspring was crossed with a zebra weighing 70
kg, the new offspring produced was 68 kg.
SEP
30
3. A tan-colored female mouse is crossed with a white-colored male mouse. All of the male
offspring produced from this cross were tan, while all of the female offspring produced by
this cross had patches of tan and white coloration.
i
tv
A Ⓡ
=
W
80
Fri Sep 30 9:13 AM
☐M
:
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education