Get started with: [STANDARD ASSESSMENT] This example uses a simple problem to demonstrate how to create a MATLAB coding problem where the student solution must be a function. Only the values returned by the function can be assessed in function problem types. This problem type can introduce confusion to students not yet comfortable writing their own functions Step 1: Use this area to set up the problem and describe the task(s) the student solution will be assessed on. For example Two commonly used scales for measuring temperature are Fahrenheit and Celsius. In this course we will often want to convert temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius. Create a function called tempF2C that will accept as input a single temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and return the equivalent temperature in degrees Celsius. Recall that Fahrenheit and Celsius are related by the following equation Te-(Ty-32)/18 Step 2: Select "Function" Problem Type below Function Save C Reset MATLAB Documentation 1% Step 4: If desired, provide template code for the student solution. 2% Clicking the lock icon prevents changes to that line of code. 3% Locking the function definition ensures the function can be called 4% correctly in the assessment tests. function tempc tempF2C (tempF) * Code your answer below
Get started with: [STANDARD ASSESSMENT] This example uses a simple problem to demonstrate how to create a MATLAB coding problem where the student solution must be a function. Only the values returned by the function can be assessed in function problem types. This problem type can introduce confusion to students not yet comfortable writing their own functions Step 1: Use this area to set up the problem and describe the task(s) the student solution will be assessed on. For example Two commonly used scales for measuring temperature are Fahrenheit and Celsius. In this course we will often want to convert temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius. Create a function called tempF2C that will accept as input a single temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and return the equivalent temperature in degrees Celsius. Recall that Fahrenheit and Celsius are related by the following equation Te-(Ty-32)/18 Step 2: Select "Function" Problem Type below Function Save C Reset MATLAB Documentation 1% Step 4: If desired, provide template code for the student solution. 2% Clicking the lock icon prevents changes to that line of code. 3% Locking the function definition ensures the function can be called 4% correctly in the assessment tests. function tempc tempF2C (tempF) * Code your answer below
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
![My Solutions >
My first FUNCTION problem
Get started with: [STANDARD ASSESSMENT]
This example uses a simple problem to demonstrate how to create a MATLAB coding problem where the student solution must be a function. Only the values returned by the
function can be assessed in function problem types. This problem type can introduce confusion to students not yet comfortable writing their own functions,
Step 1: Use this area to set up the problem and describe the task(s) the student solution will be assessed on.
For example:
Two commonly used scales for measuring temperature are Fahrenheit and Celsius. In this course we will often want to convert temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees
Celsius. Create a function called tempF2C that will accept as input a single temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and return the equivalent temperature in degrees Celsius.
Recall that Fahrenheit and Celsius are related by the following equation:
Tc (T-32)/1.8
Step 2: Select "Function" Problem Type below
Function >
Save C Reset
MATLAB Documentation
1 % Step 4: If desired, provide template code for the student solution.
2 % Clicking the lock icon prevents changes to that line of code.
3 % Locking the function definition ensures the function can be called
4 % correctly in the assessment tests.
5
6 function tempC = tempF2C (tempF)
7
% Code your answer below
8
9 end](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbed8f595-9f32-4e88-b8dd-10db80c927e5%2Ff018852c-264b-45ed-b0b1-8271b433bed1%2F2qmnddo_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:My Solutions >
My first FUNCTION problem
Get started with: [STANDARD ASSESSMENT]
This example uses a simple problem to demonstrate how to create a MATLAB coding problem where the student solution must be a function. Only the values returned by the
function can be assessed in function problem types. This problem type can introduce confusion to students not yet comfortable writing their own functions,
Step 1: Use this area to set up the problem and describe the task(s) the student solution will be assessed on.
For example:
Two commonly used scales for measuring temperature are Fahrenheit and Celsius. In this course we will often want to convert temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to degrees
Celsius. Create a function called tempF2C that will accept as input a single temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and return the equivalent temperature in degrees Celsius.
Recall that Fahrenheit and Celsius are related by the following equation:
Tc (T-32)/1.8
Step 2: Select "Function" Problem Type below
Function >
Save C Reset
MATLAB Documentation
1 % Step 4: If desired, provide template code for the student solution.
2 % Clicking the lock icon prevents changes to that line of code.
3 % Locking the function definition ensures the function can be called
4 % correctly in the assessment tests.
5
6 function tempC = tempF2C (tempF)
7
% Code your answer below
8
9 end
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
out put;
Undefined function 'tempF2C' for input arguments of type 'double'.
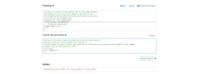
Transcribed Image Text:Function >
Save C Reset
1 % Step 4: If desired, provide template code for the student solution.
2% Clicking the lock icon prevents changes to that line of code.
3 % Locking the function definition ensures the function can be called
4 % correctly in the assessment tests.
5 fprintf('70°F = %f°C', tempF2C (70))
6 function tempC = tempF2C (tempF)
% Code your answer below
8 tempC=(tempF-32)/1.8;
9 end
10
Code to call your function >
1% Step 5: This block is used by students to run and test their function.
2 % A test scenario is often provided by the instructor.
3 % NOTE: Update the default function name (myFunction) to be the name of the student function (tempF2C in this example)
4 % Next: click on "+Add Assessment" below
tF = 212;
6 tC= tempF2C (tF)
Output
Undefined function 'tempF2C' for input arguments of type 'double'.
MATLAB Documentation
C Reset
▶ Run Function ?
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY