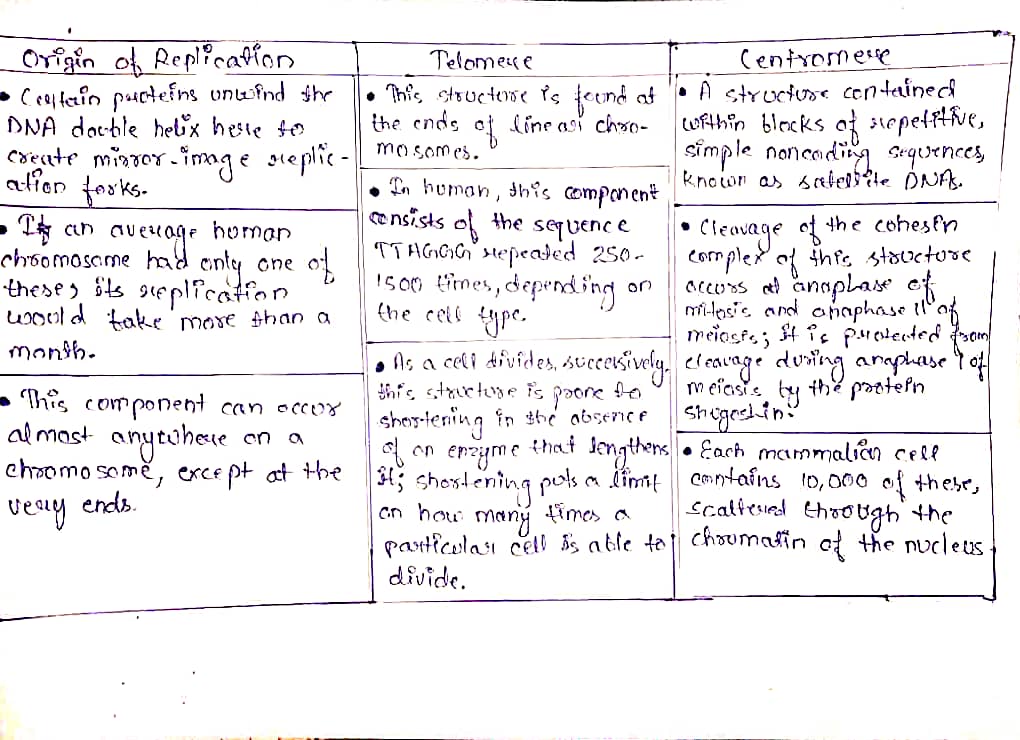
Origins of replication, centromeres, and telomeres are all involved in replication and segregation of chromosomes. Classify each statement below under the structure it describes. Each mammalian cell contains 10,000 of these, scattered through the chromatin of the nucleus. As a cell divides successively, this structure is prone to shortening in the absence of an enzyme that lengthens it; shortening puts a limit on how many times a particular cell is able to divide. If an average human chromosome had only one of these, its replication would take more than a month. Origin of replication Certain proteins unwind the DNA double helix here to create mirror- image replication forks. In humans, this component consists of the sequence TTAGGG repeated 250-1500 times, depending on the cell type. This component can occur almost anywhere on a chromosome, except at the very ends. Telomere This structure is found at the ends of linear chromosomes. Cleavage of the cohesin complex of this structure occurs at anaphase of mitosis and anaphase Il of meiosis; it is protected from cleavage during anaphase I of meiosis by the protein Shugoshin. A structure contained within blocks of repetitive, simple noncoding sequences, known as satellite DNAs. Centromere
Bacterial Genomics
The study of the morphological, physiological, and evolutionary aspects of the bacterial genome is referred to as bacterial genomics. This subdisciplinary field aids in understanding how genes are assembled into genomes. Further, bacterial or microbial genomics has helped researchers in understanding the pathogenicity of bacteria and other microbes.
Transformation Experiment in Bacteria
In the discovery of genetic material, the experiment conducted by Frederick Griffith on Streptococcus pneumonia proved to be a stepping stone.
Plasmids and Vectors
The DNA molecule that exists in a circular shape and is smaller in size which is capable of its replication is called Plasmids. In other words, it is called extra-chromosomal plasmid DNA. Vectors are the molecule which is capable of carrying genetic material which can be transferred into another cell and further carry out replication and expression. Plasmids can act as vectors.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









