On the circuit shown below: 1. Determine the voltage V1 2. Determine the voltage across each of the resistors 3. Determine the current through each of the resistors Determine the power delivered to each of the resistors. 4. 0's 5 mA V₁ HIPE R₁ 4 ΚΩ R₂ ΣΚΩ www R3 4 ΚΩ 0
On the circuit shown below: 1. Determine the voltage V1 2. Determine the voltage across each of the resistors 3. Determine the current through each of the resistors Determine the power delivered to each of the resistors. 4. 0's 5 mA V₁ HIPE R₁ 4 ΚΩ R₂ ΣΚΩ www R3 4 ΚΩ 0
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Circuit Analysis Challenge**
In the circuit diagram provided, please complete the following tasks:
1. **Determine the voltage \( V_1 \).**
2. **Calculate the voltage across each resistor.**
3. **Find the current through each resistor.**
4. **Determine the power delivered to each resistor.**
**Circuit Description:**
- A current source \( I_s = 5 \, \text{mA} \) is connected in series with three resistors: \( R_1 = 4 \, \text{k}\Omega \), \( R_2 = 2 \, \text{k}\Omega \), and \( R_3 = 4 \, \text{k}\Omega \).
- The resistors \( R_2 \) and \( R_3 \) are connected in series, forming a branch parallel to \( R_1 \).
- The circuit is grounded at one point, creating a reference point of \( 0 \, \text{V} \).
Use this information to perform the calculations and understand the behavior of circuits involving resistors and current sources.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given question
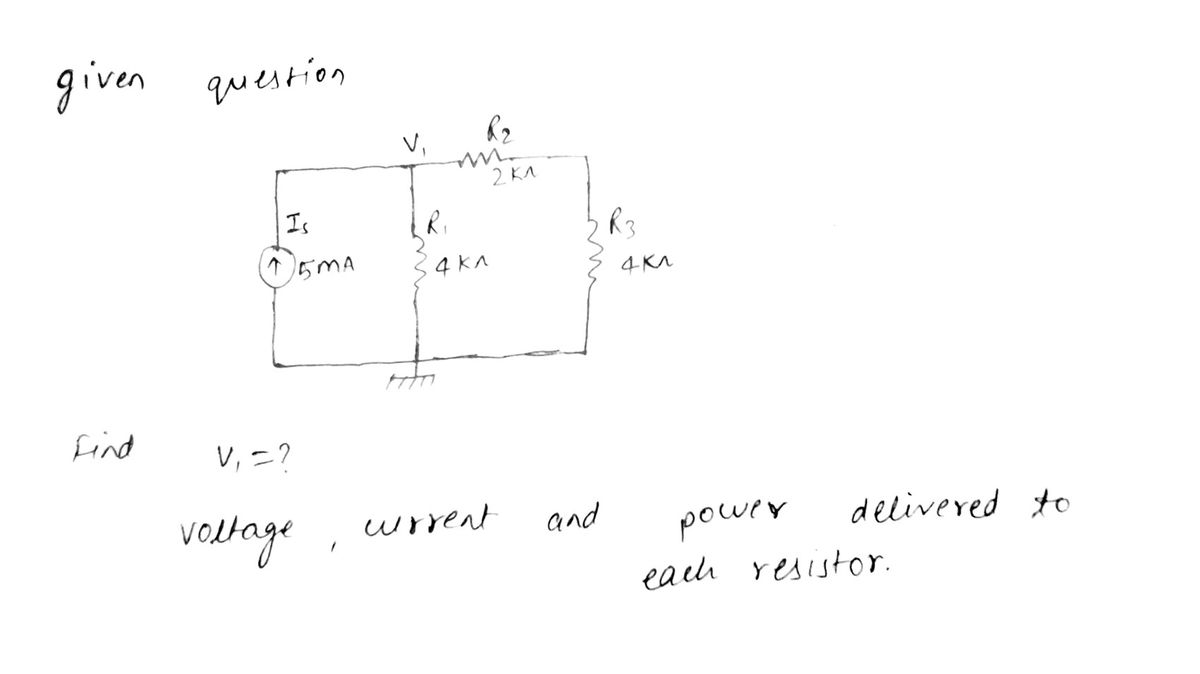
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,