Nuclear Decay Equations Learning Goal: To predict the products of alpha emission, beta emission, positron emission, and electron capture. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus. There are five major types of radioactive decay: 1. Alpha (a) radiation consists of helium nuclei. The helium nucleus is a small particle containing two protons and two neutrons (He). 2. Beta (3) radiation consists of electrons. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a beta particle using superscripts and subscripts is ºe. 3. Positron emission results from the conversion of a proton in the nucleus to a neutron. The ejected positron is a particle that has the same mass as an electron but an opposite charge. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a positron using superscripts and subscripts is º is je 4. Electron capture is the capture of an inner shell electron by a proton in the nucleus. The process emits gamma (y) radiation and results in a proton converting to a neutron. Gamma radiation consists of high- energy electromagnetic radiation. 5. Gamma (y) radiation consists of high- energy radiation, and contains no particles and thus they have no mass. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing gamma radiation using superscripts and subscripts is y ▼ Part A Identify the nuclide produced when neptunium-237 decays by alpha emission: 23 Np He + ? Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Submit A chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Part B ΑΣΦ 1 0 ? Identify the nuclide produced when thorium-234 decays by beta emission: The + ? Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts. View Available Hint(s) ΑΣΦ A chemical reaction does not occur for this question. 3 of 43 Review | Constants | Periodic Table
Nuclear Decay Equations Learning Goal: To predict the products of alpha emission, beta emission, positron emission, and electron capture. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus. There are five major types of radioactive decay: 1. Alpha (a) radiation consists of helium nuclei. The helium nucleus is a small particle containing two protons and two neutrons (He). 2. Beta (3) radiation consists of electrons. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a beta particle using superscripts and subscripts is ºe. 3. Positron emission results from the conversion of a proton in the nucleus to a neutron. The ejected positron is a particle that has the same mass as an electron but an opposite charge. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a positron using superscripts and subscripts is º is je 4. Electron capture is the capture of an inner shell electron by a proton in the nucleus. The process emits gamma (y) radiation and results in a proton converting to a neutron. Gamma radiation consists of high- energy electromagnetic radiation. 5. Gamma (y) radiation consists of high- energy radiation, and contains no particles and thus they have no mass. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing gamma radiation using superscripts and subscripts is y ▼ Part A Identify the nuclide produced when neptunium-237 decays by alpha emission: 23 Np He + ? Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts. ▸ View Available Hint(s) Submit A chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Part B ΑΣΦ 1 0 ? Identify the nuclide produced when thorium-234 decays by beta emission: The + ? Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts. View Available Hint(s) ΑΣΦ A chemical reaction does not occur for this question. 3 of 43 Review | Constants | Periodic Table
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
![**Nuclear Decay Equations**
**Learning Goal**:
To predict the products of alpha emission, beta emission, positron emission, and electron capture.
**Radioactivity** is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus. There are five major types of radioactive decay:
1. **Alpha (α) radiation** consists of helium nuclei. The helium nucleus is a small particle containing two protons and two neutrons \((^4_2\text{He})\).
2. **Beta (β) radiation** consists of electrons. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a beta particle using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_{-1}e)\).
3. **Positron emission** results from the conversion of a proton in the nucleus to a neutron. The ejected positron is a particle that has the same mass as an electron but an opposite charge. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a positron using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_{+1}e)\).
4. **Electron capture** is the capture of an inner shell electron by a proton in the nucleus. The process emits gamma (γ) radiation and results in a proton converting to a neutron. Gamma radiation consists of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
5. **Gamma (γ) radiation** consists of high-energy radiation, and contains no particles and thus they have no mass. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing gamma radiation using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_0\gamma)\).
### Part A
Identify the nuclide produced when neptunium-237 decays by alpha emission:
\[
^{237}_{93}\text{Np} \rightarrow {^4_2\text{He}} + ?
\]
Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts.
**Hint Section**: View available hints by expanding this section.
**Input Tool**: Use the provided input box for submission.
**Checkbox**: Option to check if a chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
**Submit Button**: Finalize your answer by clicking "Submit".
---
### Part B
Identify the nuclide produced when thorium-234 decays by beta emission:
\[
^{234}_{90}\text{Th} \rightarrow {^0_{-1}e} + ?
\]
Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts.
**Hint Section**:](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F293c8ac7-d65e-4987-88ce-2abf44da1ee7%2F4dd291c1-27ed-456f-b8a3-855a1a230017%2Fl9b1y1_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Nuclear Decay Equations**
**Learning Goal**:
To predict the products of alpha emission, beta emission, positron emission, and electron capture.
**Radioactivity** is the spontaneous emission of radiation from an unstable nucleus. There are five major types of radioactive decay:
1. **Alpha (α) radiation** consists of helium nuclei. The helium nucleus is a small particle containing two protons and two neutrons \((^4_2\text{He})\).
2. **Beta (β) radiation** consists of electrons. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a beta particle using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_{-1}e)\).
3. **Positron emission** results from the conversion of a proton in the nucleus to a neutron. The ejected positron is a particle that has the same mass as an electron but an opposite charge. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing a positron using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_{+1}e)\).
4. **Electron capture** is the capture of an inner shell electron by a proton in the nucleus. The process emits gamma (γ) radiation and results in a proton converting to a neutron. Gamma radiation consists of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
5. **Gamma (γ) radiation** consists of high-energy radiation, and contains no particles and thus they have no mass. In nuclear equations, the standard format for representing gamma radiation using superscripts and subscripts is \((^0_0\gamma)\).
### Part A
Identify the nuclide produced when neptunium-237 decays by alpha emission:
\[
^{237}_{93}\text{Np} \rightarrow {^4_2\text{He}} + ?
\]
Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts.
**Hint Section**: View available hints by expanding this section.
**Input Tool**: Use the provided input box for submission.
**Checkbox**: Option to check if a chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
**Submit Button**: Finalize your answer by clicking "Submit".
---
### Part B
Identify the nuclide produced when thorium-234 decays by beta emission:
\[
^{234}_{90}\text{Th} \rightarrow {^0_{-1}e} + ?
\]
Express your answer as an isotope using prescripts.
**Hint Section**:
Expert Solution
Step 1
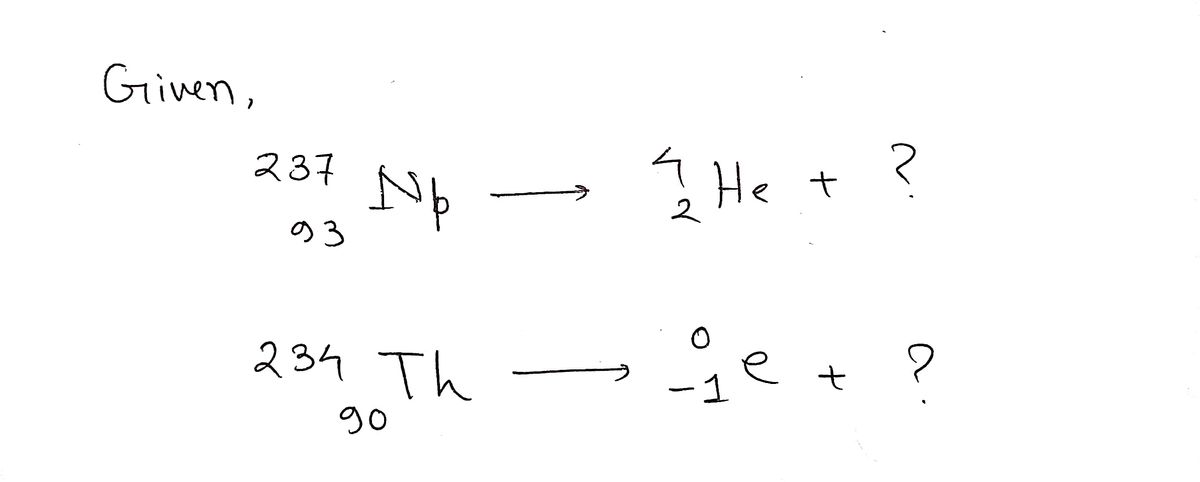
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY