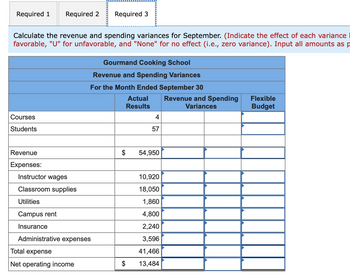
The Gourmand Cooking School runs short cooking courses at its small campus. Management has identified two cost drivers it uses in its budgeting and performance reports-the number of courses and the total number of students. For example, the school might run two courses in a month and have a total of 65 students enrolled in those two courses. Data concerning the company's cost formulas appear below: Instructor wages Classroom supplies Utilities Campus rent Insurance Administrative expenses Fixed Cost per Month $ 1,210 $ 4,800 Revenue Instructor wages Classroom supplies Utilities Campus rent Insurance Administrative expenses $ 2,100 $ 3,600 Cost per Course $ 2,910 $ 60 Cost per Student $ 280 $ 45 For example, administrative expenses should be $3,600 per month plus $45 per course plus $6 per student. The company's sales should average $890 per student. Actual $ 54,950 $ 10,920 $ 18,050 $ 1,860 $ 4,800 $ 2,240 $ 3,596 The company planned to run four courses with a total of 65 students; however, it actually ran four courses with a total of only 57 students. The actual operating results for September appear below: $6 Required: 1. Prepare the company's planning budget for September. 2. Prepare the company's flexible budget for September. 3. Calculate the revenue and spending variances for September.
Master Budget
A master budget can be defined as an estimation of the revenue earned or expenses incurred over a specified period of time in the future and it is generally prepared on a periodic basis which can be either monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or annually. It helps a business, an organization, or even an individual to manage the money effectively. A budget also helps in monitoring the performance of the people in the organization and helps in better decision-making.
Sales Budget and Selling
A budget is a financial plan designed by an undertaking for a definite period in future which acts as a major contributor towards enhancing the financial success of the business undertaking. The budget generally takes into account both current and future income and expenses.
Im having trouble with this accounting problem.


Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

im curious how to fill this out correcly.