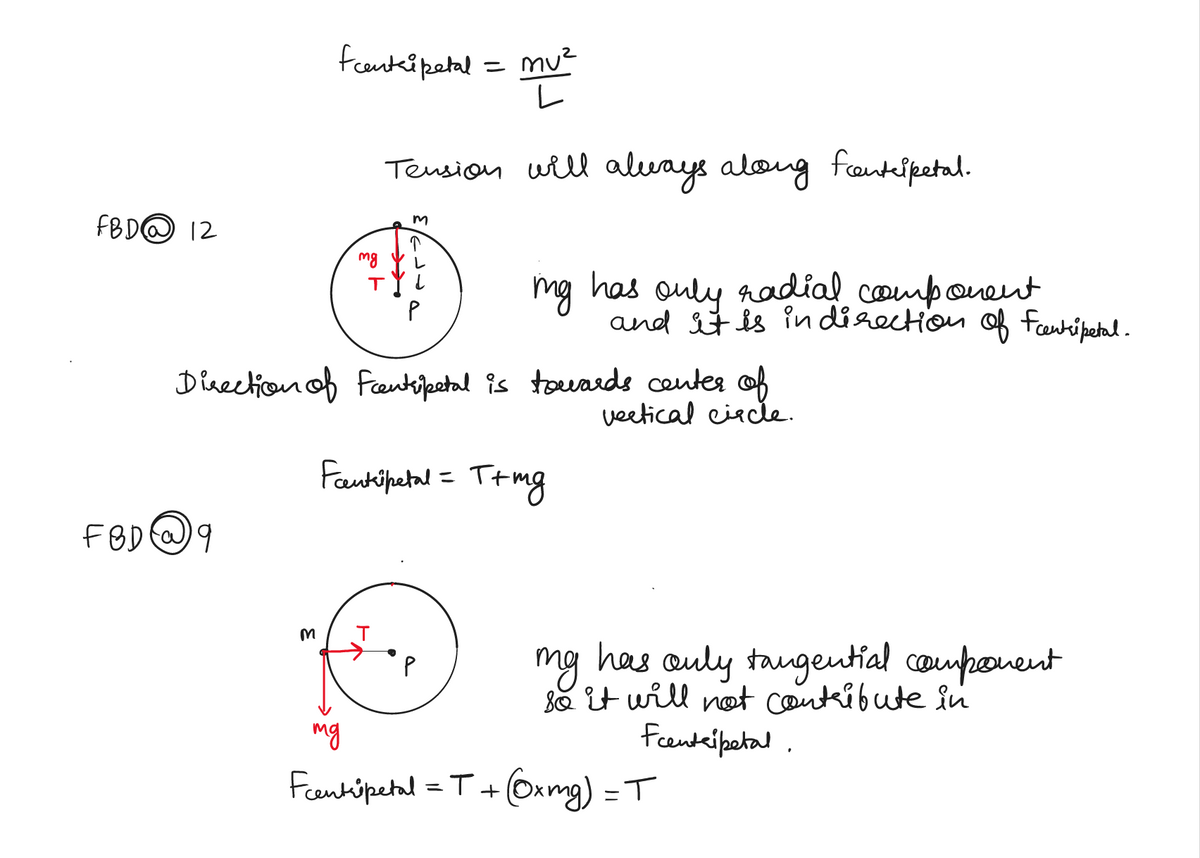
Near the surface of the earth, a mass m which is fastened to a cord of length L is rotating around point P in a vertical circle as shown. If the mass is at each of the following "clock time positions: 12, 9, 10, 6, draw an FBD and indicate what force and/or components of forces can be labeled as centripetal in each case. Your answer should be in terms of the tension T and mg. 11 8 12 2 3 FBD @12 mv² = FBD @9 FBD @10 FBD
Gravitational force
In nature, every object is attracted by every other object. This phenomenon is called gravity. The force associated with gravity is called gravitational force. The gravitational force is the weakest force that exists in nature. The gravitational force is always attractive.
Acceleration Due to Gravity
In fundamental physics, gravity or gravitational force is the universal attractive force acting between all the matters that exist or exhibit. It is the weakest known force. Therefore no internal changes in an object occurs due to this force. On the other hand, it has control over the trajectories of bodies in the solar system and in the universe due to its vast scope and universal action. The free fall of objects on Earth and the motions of celestial bodies, according to Newton, are both determined by the same force. It was Newton who put forward that the moon is held by a strong attractive force exerted by the Earth which makes it revolve in a straight line. He was sure that this force is similar to the downward force which Earth exerts on all the objects on it.
![**Educational Content: Understanding Circular Motion**
**Scenario Overview:**
Near the surface of the Earth, a mass \( m \) is fastened to a cord of length \( L \), rotating in a vertical circle around point \( P \). This exercise involves analyzing the forces acting on the mass at specific positions in its path, which mimic clock positions: 12, 9, 10, and 6.
**Objective:**
For each specified position (12, 9, 10, and 6), draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) to illustrate the forces acting on the mass, \( m \). Identify and label the centripetal forces in terms of tension \( T \) and gravitational force \( mg \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram features a vertical circular path with labeled numbers representing clock positions. Point \( P \) is at the center of the circle, and the mass \( m \) moves along this path with a cord of length \( L \).
1. **FBD @ 12:**
- The mass is at the top of the circle.
- Forces: Gravity (\( mg \)) acts downward, and tension (\( T \)) acts downward along the cord.
2. **FBD @ 9:**
- The mass is at the 9 o'clock position.
- Forces: Gravity (\( mg \)) acts downward, and tension (\( T \)) acts horizontally toward the center.
3. **FBD @ 10:**
- The mass is between 9 and 12.
- Forces: Gravity (\( mg \)) acts downward, while tension (\( T \)) acts along the diagonal, pointing towards the center.
4. **FBD @ 6:**
- The mass is at the bottom of the circle.
- Forces: Gravity (\( mg \)) acts downward, and tension (\( T \)) acts upward, providing more tension to counteract gravity.
**Mathematical Expression:**
The centripetal force required to maintain the mass in circular motion is:
\[
m v^2 / L
\]
This expression equates the radial tension and gravitational components contributing to the centripetal force in the vertical circle.
**Conclusion:**
By analyzing these positions, one can understand how gravitational force and tension maintain circular motion, varying with the object's position in the circle. This fundamental principle applies to many real-world scenarios,](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F74c7a7c3-55af-48fc-bd21-d0ca6e46b4b9%2F0de6e89e-7586-4875-a5ec-eda8950cb462%2F8btli8a9_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









