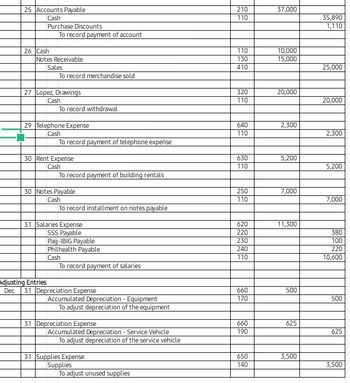
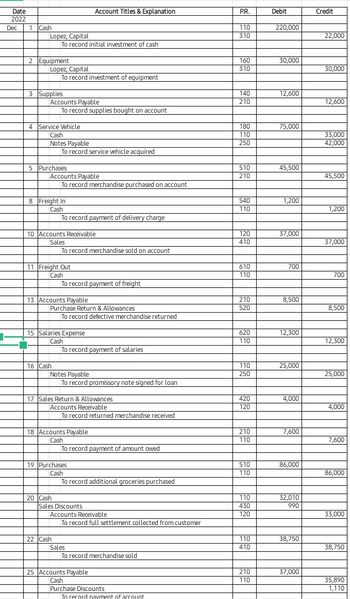
Mr. Juan Lopez launched Lopez Fiesta Mart on December 1, 2022 with a cash investment of ₱220,000. The following are additional transactions for the month: 2 Mr. Lopez invested equipment for the business worth ₱30,000. 3 Bought supplies on account for ₱12,600. 4 Acquired a service vehicle costing ₱75,000. A payment of ₱33,000 cash was made and a promissory note was given for the remainder, payable for 6 equal monthly installment. 5 Purchased merchandise from JKL Enterprises ₱45,500, Term, 3/20, n/30. 8 Paid ₱1,200 delivery charge for December 5 purchase. 10 Sold merchandise on account ₱37,000, Term, 3/10, n/30. Cost of Merchandise, ₱25,000. 11 Paid ₱700 freight for December 10 transaction. 13 Returned defective merchandise to JKL Enterprises amounting to ₱8,500. 15 Paid salaries, ₱12,300 16 Signed a promissory note for ₱25,000 loaned amount from Commonwealth Bank. 17 Received returned merchandise from customers on December 10, ₱4,000. 18 Paid ₱7,600 of the amount owed from the December 3 transaction. 19 Purchase additional groceries from QR Supermarket amounting to ₱86,000. 20 Collected full settlement of customer from December 10 sale. 22 ₱21,450 cost of merchandise was sold for ₱38,750. 25 Settled account to JKL Enterprises. 26 Cash received, ₱10,000 and a promissory note for ₱25,000 for merchandise sold to a key customer. Cost of merchandise, ₱28,000. 27 Mr. Lopez withdrew ₱20,000 cash from the business. 29 Paid telephone expense, ₱2,300. 30 Paid building rentals for the month, ₱5,200. 30 Paid the first installment of the note payable on Service Vehicle. 31 Paid Salaries ₱11,300, net of the following deductions: SSS, ₱380; Pag-IBIG, ₱100; Philhealth, ₱220 The Merchandise Inventory at the end of the of the month is ₱48,000. Additional information for year-end adjustments. Ø The useful life of the equipment is 5 years with no salvage value. -The useful life of the service vehicle is 10 years with no salvage value. -Remaining unused supplies worth ₱9,100. Use asset method. Question: 1. Prepare General Ledger
The Effect Of Prepaid Taxes On Assets And Liabilities
Many businesses estimate tax liability and make payments throughout the year (often quarterly). When a company overestimates its tax liability, this results in the business paying a prepaid tax. Prepaid taxes will be reversed within one year but can result in prepaid assets and liabilities.
Final Accounts
Financial accounting is one of the branches of accounting in which the transactions arising in the business over a particular period are recorded.
Ledger Posting
A ledger is an account that provides information on all the transactions that have taken place during a particular period. It is also known as General Ledger. For example, your bank account statement is a general ledger that gives information about the amount paid/debited or received/ credited from your bank account over some time.
Trial Balance and Final Accounts
In accounting we start with recording transaction with journal entries then we make separate ledger account for each type of transaction. It is very necessary to check and verify that the transaction transferred to ledgers from the journal are accurately recorded or not. Trial balance helps in this. Trial balance helps to check the accuracy of posting the ledger accounts. It helps the accountant to assist in preparing final accounts. It also helps the accountant to check whether all the debits and credits of items are recorded and posted accurately. Like in a balance sheet debit and credit side should be equal, similarly in trial balance debit balance and credit balance should tally.
Adjustment Entries
At the end of every accounting period Adjustment Entries are made in order to adjust the accounts precisely replicate the expenses and revenue of the current period. It is also known as end of period adjustment. It can also be referred as financial reporting that corrects the errors made previously in the accounting period. The basic characteristics of every adjustment entry is that it affects at least one real account and one nominal account.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Mr. Juan Lopez launched Lopez Fiesta Mart on December 1, 2022 with a cash investment of ₱220,000. The following are additional transactions for the month: 2Mr. Lopez invested equipment for the business worth ₱30,000. 3Bought supplies on account for ₱12,600. 4Acquired a service vehicle costing ₱75,000. A payment of ₱33,000 cash was made and a promissory note was given for the remainder, payable for 6 equal monthly installment. 5Purchased merchandise from JKL Enterprises ₱45,500, Term, 3/20, n/30. 8Paid ₱1,200 delivery charge for December 5 purchase. 10Sold merchandise on account ₱37,000, Term, 3/10, n/30. Cost of Merchandise, ₱25,000. 11Paid ₱700 freight for December 10 transaction. 13Returned defective merchandise to JKL Enterprises amounting to ₱8,500. 15Paid salaries, ₱12,300 16Signed a promissory note for ₱25,000 loaned amount from Commonwealth Bank. 17Received returned merchandise from customers on December 10, ₱4,000. 18Paid ₱7,600 of the amount owed from the December 3 transaction. 19Purchase additional groceries from QR Supermarket amounting to ₱86,000. 20Collected full settlement of customer from December 10 sale. 22₱21,450 cost of merchandise was sold for ₱38,750. 25Settled account to JKL Enterprises. 26Cash received, ₱10,000 and a promissory note for ₱25,000 for merchandise sold to a key customer. Cost of merchandise, ₱28,000. 27Mr. Lopez withdrew ₱20,000 cash from the business. 29Paid telephone expense, ₱2,300. 30Paid building rentals for the month, ₱5,200. 30Paid the first installment of the note payable on Service Vehicle. 31Paid Salaries ₱11,300, net of the following deductions: SSS, ₱380; Pag-IBIG, ₱100; Philhealth, ₱220 The Merchandise Inventory at the end of the of the month is ₱48,000. Additional information for year-end adjustments. Ø The useful life of the equipment is 5 years with no salvage value. -The useful life of the service vehicle is 10 years with no salvage value. -Remaining unused supplies worth ₱9,100. Use asset method.
Question:
1. Prepare the General Ledger. Pls use periodic inventory method.