Bacterial Morphology
The bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that are single-celled, and are found to exist as free-living and possess a microscopic size. The morphology is found to vary in the bacteria, where some of them are identified as individual organisms and the others are detected as colonies. The size and shape of the bacterial cell also represent its morphology.
Bacterial cell structure
Bacteria are single-celled, tiny creatures that may enter healthy tissues and grow rapidly. Bacteria are microscopic organisms that are tiny and unicellular. These are members of the prokaryote kingdom. They live in water, air, soil, and all-natural environments. They are used in industrial and therapeutic processes, and they support a wide range of plant and animal life. The first organism to appear on the planet. Bacteria-like creatures are the oldest known fossils. Bacteria can consume a wide range of organic and inorganic elements, and some may even survive in harsh conditions.
mitochondria definition
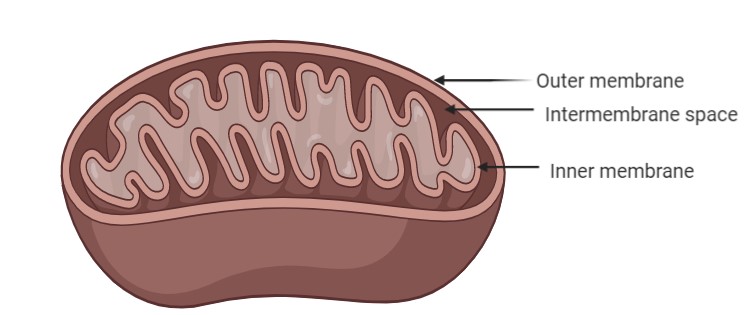
They have their own DNA which is similar to bacterial DNA. They have ribosomes, enzymes and transport systems which are similar to those in bacteria. They produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). They are also involved in the storage of calcium, heat generation. They can be spherical/cylindrical or branched. It has an inner and an outer membrane separated by an intermembrane space. The matrix of the mitochondria has double stranded DNA which is mostly circular. It mostly shows maternal inheritance because the paternal mitochondria are destroyed by the enzymes in the egg on fertilization.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









