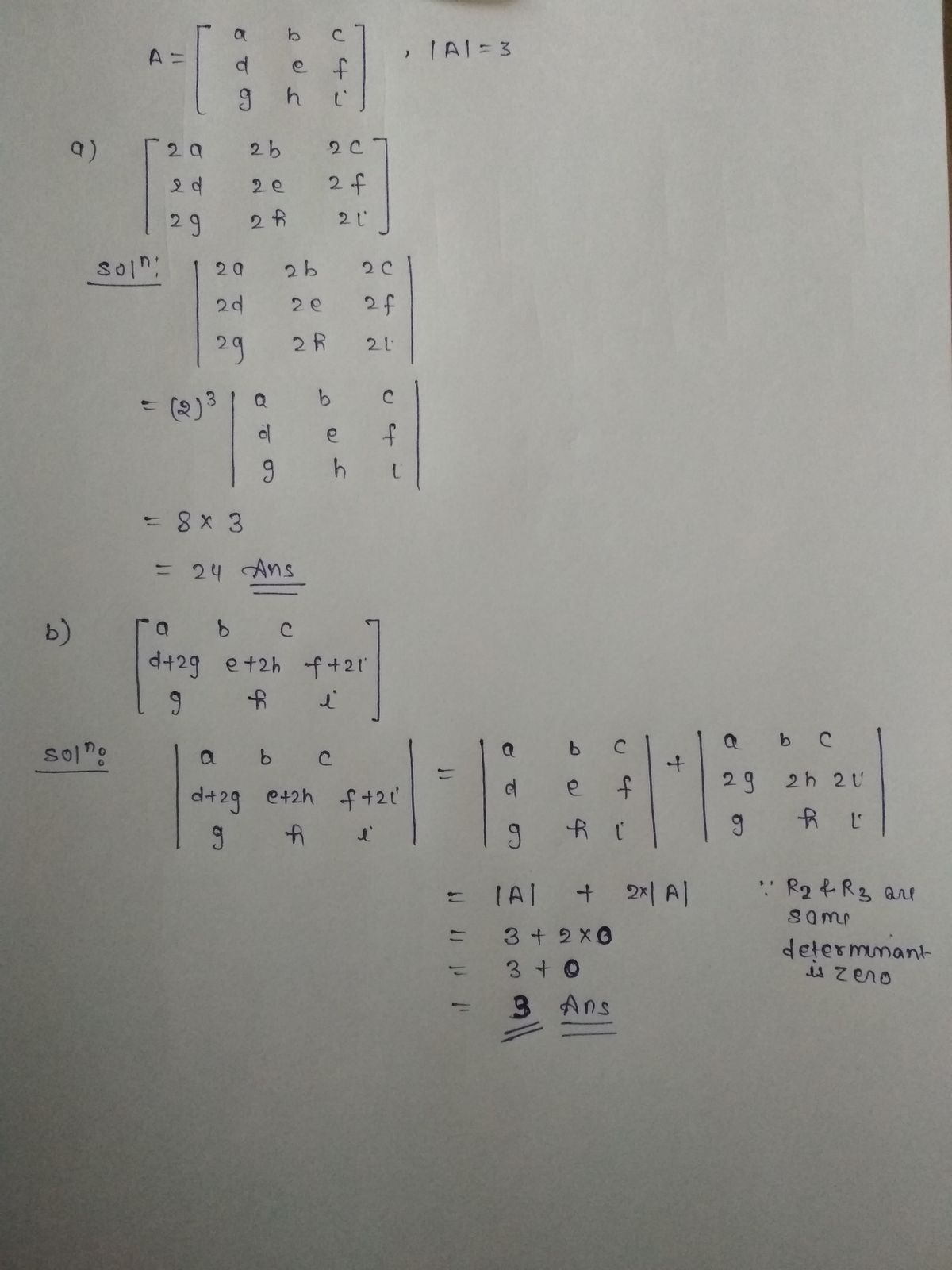
minants below. (a) (b) Suppose A = (c) 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f 2g 2h 2i a d+ 2g 9 b e+ 2h b e a b с d e f and detA= 3. Determine the value of the deter- gh i C f+ 2i i a d 4g + d 4h+e_4i+ f C f
minants below. (a) (b) Suppose A = (c) 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f 2g 2h 2i a d+ 2g 9 b e+ 2h b e a b с d e f and detA= 3. Determine the value of the deter- gh i C f+ 2i i a d 4g + d 4h+e_4i+ f C f
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
100%
![**Educational Content on Determinants**
Consider the matrix \( A \):
\[
A = \begin{bmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & e & f \\ g & h & i \end{bmatrix}
\]
Given that \( \text{det} A = 3 \), we are tasked with determining the value of the determinants of the following matrices:
(a)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
2a & 2b & 2c \\
2d & 2e & 2f \\
2g & 2h & 2i
\end{vmatrix}
\]
(b)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
a & b & c \\
d + 2g & e + 2h & f + 2i \\
g & h & i
\end{vmatrix}
\]
(c)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
a & b & c \\
d & e & f \\
4g + d & 4h + e & 4i + f
\end{vmatrix}
\]
### Explanation of Determinants
- The determinant of a matrix provides valuable information about the matrix, including whether it's invertible and its scaling factor in linear transformations.
- When scaling all elements of a row or column in a determinant, the determinant itself is scaled by that factor.
- Adding or multiplying rows by constants can also affect the determinant in predictable ways according to properties of determinants.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F04927cb6-da1d-4c0a-85f6-9ebffa5c5f13%2Ffcdc898c-435e-440a-9beb-056cd0fa6eff%2Fvf122jr_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content on Determinants**
Consider the matrix \( A \):
\[
A = \begin{bmatrix} a & b & c \\ d & e & f \\ g & h & i \end{bmatrix}
\]
Given that \( \text{det} A = 3 \), we are tasked with determining the value of the determinants of the following matrices:
(a)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
2a & 2b & 2c \\
2d & 2e & 2f \\
2g & 2h & 2i
\end{vmatrix}
\]
(b)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
a & b & c \\
d + 2g & e + 2h & f + 2i \\
g & h & i
\end{vmatrix}
\]
(c)
\[
\begin{vmatrix}
a & b & c \\
d & e & f \\
4g + d & 4h + e & 4i + f
\end{vmatrix}
\]
### Explanation of Determinants
- The determinant of a matrix provides valuable information about the matrix, including whether it's invertible and its scaling factor in linear transformations.
- When scaling all elements of a row or column in a determinant, the determinant itself is scaled by that factor.
- Adding or multiplying rows by constants can also affect the determinant in predictable ways according to properties of determinants.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

