A steel beam, of lengths a=4 m and b=4 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q=0 kN/m to q=4.2 kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q=4.2 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa. y, v q A Part B a 5 mm 200 mm Дв 300 mm b C Figure Q.1 d) the maximum normal stress in the cross-section of the beam. Enter the positive value of the stress. Enter your answer in MPa to two decimal places. Perform double integration of the bending moment equations. You will obtain deflections in this form: for 0≤x≤ a vEI = F(x) + C₁ x + C3 vEI = G(x) + C₂x + C4 for a ≤ x ≤a+b Calculate: e) the value of the integration constant C₂. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places. f) the value of the integration constant C4. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places.
A steel beam, of lengths a=4 m and b=4 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q=0 kN/m to q=4.2 kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q=4.2 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa. y, v q A Part B a 5 mm 200 mm Дв 300 mm b C Figure Q.1 d) the maximum normal stress in the cross-section of the beam. Enter the positive value of the stress. Enter your answer in MPa to two decimal places. Perform double integration of the bending moment equations. You will obtain deflections in this form: for 0≤x≤ a vEI = F(x) + C₁ x + C3 vEI = G(x) + C₂x + C4 for a ≤ x ≤a+b Calculate: e) the value of the integration constant C₂. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places. f) the value of the integration constant C4. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Could you please help me answer these questions. thank you

Transcribed Image Text:A steel beam, of lengths a=4 m and b=4 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B, see Figure Q.1. The width and
height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the
intensity that linearly varies from q = 0 kN/m to q= 4.2 kN/m for AB span; and is constant with q= 4.2 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa.
Y, V
9
A
Part B
a
5 mm
200 mm
300 mm
B
b
с
Figure Q.1
d) the maximum normal stress in the cross-section of the beam. Enter the positive value of the stress. Enter your answer in MPa to two
decimal places.
Perform double integration of the bending moment equations. You will obtain deflections in this form:
VEI = F(x) + C₁x + C3
for 0 ≤ x ≤ a
VEI = G(x) + C₂x + C4
for a ≤x≤ a + b
Calculate:
e) the value of the integration constant C₂. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places.
f) the value of the integration constant C4. Enter your answer in kNm² to three decimal places.
g) the value of the deflection at point C. Enter your answer in mm to three decimal places. Assume the positive direction of deflection in the
positive direction of v axis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 33 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Could you answer question G.
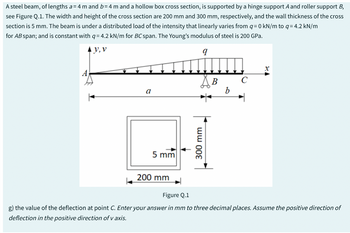
Transcribed Image Text:A steel beam, of lengths a= 4 m and b= 4 m and a hollow box cross section, is supported by a hinge support A and roller support B,
see Figure Q.1. The width and height of the cross section are 200 mm and 300 mm, respectively, and the wall thickness of the cross
section is 5 mm. The beam is under a distributed load of the intensity that linearly varies from q=0 kN/m to q= 4.2 kN/m
for AB span; and is constant with q= 4.2 kN/m for BC span. The Young's modulus of steel is 200 GPa.
V, V
یییییللللقصف
a
5 mm
200 mm
300 mm
B
b
Figure Q.1
g) the value of the deflection at point C. Enter your answer in mm to three decimal places. Assume the positive direction of
deflection in the positive direction of v axis.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY