Mary and her sister are playing with a cardboard box on the neighborhood hill. Mary climbs into the box, the total mass of the box with Mary in it is 115 kg. The box starts at rest at the beginning of the incline. The hill is at an incline of 28 degrees with respect to the horizontal.The static and kinectic friction between the box and hill is 0.4 and 0.2 respectively. Assume the box is sliding downhill. a. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the box? (same as Problem 3b) b. If the hill is 5m tall, what is the Mary's speed when she reaches the bottom? c. At the bottom of the hill, the ground becomes level, but the coefficients of friction do not change. How far will Mary slide before she comes to a stop?
Mary and her sister are playing with a cardboard box on the neighborhood hill. Mary climbs into the box, the total mass of the box with Mary in it is 115 kg. The box starts at rest at the beginning of the incline. The hill is at an incline of 28 degrees with respect to the horizontal.The static and kinectic friction between the box and hill is 0.4 and 0.2 respectively. Assume the box is sliding downhill.
a. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the box? (same as Problem 3b)
b. If the hill is 5m tall, what is the Mary's speed when she reaches the bottom?
c. At the bottom of the hill, the ground becomes level, but the coefficients of
friction do not change. How far will Mary slide before she comes to a stop?
(a)
Draw the free body diagram:
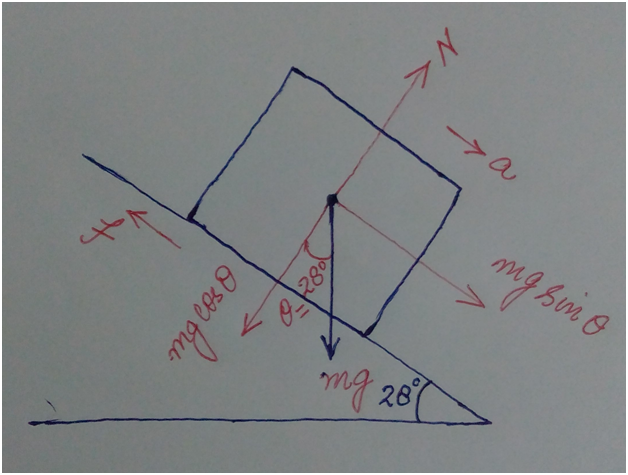
Apply Newtons second law in vertical direction direction:
Apply newtons law in horizontal direction:
Enter the required data in equation (2):
(b)
Find the length (s) of the incline:
Find the velocity at the end of incline as follows:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









