College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
Looking at these resistors in parallel, what would be the current on resister R, if the battery voltage V= 6.17 V. R= 4.66 Ω.

Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates a parallel circuit consisting of three resistors connected to a voltage source. Here's a detailed breakdown:
1. **Resistors:**
- The top resistor has a resistance of \(3 \, \Omega\).
- The middle resistor is labeled as \(R\), indicating its resistance is unknown or variable.
- The bottom resistor has a resistance of \(4 \, \Omega\).
2. **Voltage Source:**
- A voltage source is connected below the resistors, labeled with a \(V\) to denote voltage.
- It has a positive (+) and a negative (-) terminal, showing the direction of current flow.
3. **Connections:**
- The resistors are arranged in parallel, meaning there are multiple paths for current to flow.
- Each resistor is connected at both ends to the common nodes, forming parallel branches.
This diagram is useful for analyzing parallel circuits in educational settings, focusing on concepts like equivalent resistance and current distribution in parallel networks.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given data
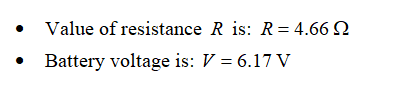
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON