Labeled graph #1 B E D 3 L K
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
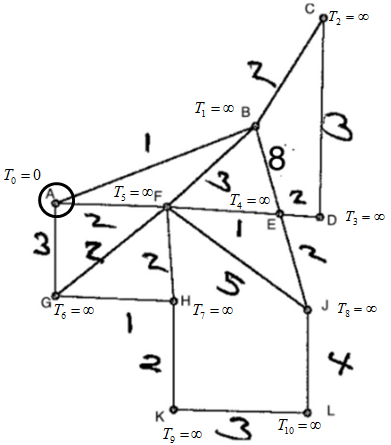
In Figure #1 use an algorithm starting from vertex A to find the shortest path to any other vertex

Transcribed Image Text:**Labeled Graph #1 Explanation**
This diagram is a connected graph consisting of twelve vertices labeled from A to L, and various edges with associated weights between the vertices.
- **Vertices and Connections:**
- Vertex A connects to B, F, and G.
- Vertex B connects to A, C, D, and F.
- Vertex C connects to B.
- Vertex D connects to B and E.
- Vertex E connects to D, F, and J.
- Vertex F connects to A, B, E, and H.
- Vertex G connects to A and H.
- Vertex H connects to F, G, and K.
- Vertex J connects to E and L.
- Vertex K connects to H and L.
- Vertex L connects to J and K.
- **Edge Weights:**
- AB: 1
- AC: 2
- AD: 3
- AF: 2
- AG: 3
- BF: 3
- BD: 2
- BE: 2
- CE: 3
- DE: 2
- EF: 1
- EJ: 5
- FG: 2
- FH: 2
- GH: 1
- HJ: 1
- HK: 2
- JL: 4
- KL: 3
This graph can be used to study pathfinding, network flow, or other graph theory concepts by analyzing the connections and edge weights.
Expert Solution
Solution:
Assign every node buy a tentative distance value: set the initial node to 0 and to all other nodes to infinity. Set the initial node as current.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

