L んー h air
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
100%

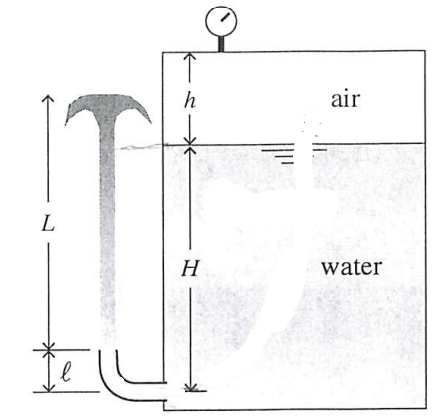
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates a cylindrical tank filled with water and covered by air at the top. A manometer is attached to measure the pressure of the air above the water. Here are the key elements:
1. **Water Tank**:
- The tank contains water up to a height of \( H \).
- Above the water, there is a column of air with a height \( h \).
2. **Manometer**:
- A pressure gauge is present at the top to measure the air pressure inside the tank.
3. **Attached Tube**:
- The tube is bent and open to the atmosphere at the left side.
- The tube is filled with a liquid (possibly mercury or any heavier liquid than water) up to a height \( L \).
- The height from the bottom of the tube to the liquid surface is \( \ell \).
This setup is typically used to study fluid dynamics and the behavior of liquids under pressure in closed systems. The combination of the water level and air pressure above it, along with the liquid in the tube, can be used to analyze principles like Pascal’s Law and the concept of hydrostatic pressure.

Transcribed Image Text:A pressurized tank of water is used to create a fountain, as illustrated. Assume that the water's free surface area in the tank is very large relative to the pipe's cross-sectional area, which is circular with diameter \( d = 1.0 \, \text{cm} \). The small pipe bend has height \( \ell = 10.0 \, \text{cm} \). At the instant when \( h = 0.75 \, \text{m} \), \( H = 2.5 \, \text{m} \), and the gauge measures a pressure of \( p_{\text{gauge}} = 20.0 \, \text{kPa} \), the water spray reaches a height \( L \) above the pipe exit.
Neglecting viscous effects, determine the height of the spray, \( L \).
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY