In the presence of oxygen, most living cells make ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the mitochondria. One of the major substrates that is oxidized is NADH. The overall reaction for this process is given by the equation below. NADH + H+ ¹2 O2 →→→ NAD+ + H₂O
In the presence of oxygen, most living cells make ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the mitochondria. One of the major substrates that is oxidized is NADH. The overall reaction for this process is given by the equation below. NADH + H+ ¹2 O2 →→→ NAD+ + H₂O
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Need help, please.
![### Oxidative Phosphorylation and NADH Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen, most living cells produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, a process occurring in the mitochondria. A key substrate that undergoes oxidation is NADH. The overall reaction for this process is:
\[ \text{NADH} + \text{H}^+ + \frac{1}{2} \text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{NAD}^+ + \text{H}_2\text{O} \]
**a. Identifying the Oxidizing Agent**
To determine the oxidizing agent in the reaction above, note that it is the substance that gains electrons. Here, \(\text{O}_2\) is the oxidizing agent because it is reduced to \(\text{H}_2\text{O}\).
**b. Calculating the Standard Electrode Potential (\(E^o'\))**
Using the half-reactions and their standard electrode potentials:
1. \( \text{NAD}^+ + \text{H}^+ + 2 \text{e}^- \rightarrow \text{NADH}, \quad E^o' = -0.320 \, \text{V} \)
2. \( \frac{1}{2} \text{O}_2 + 2 \text{H}^+ + 2 \text{e}^- \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O}, \quad E^o' = 0.816 \, \text{V} \)
**c. Calculating the Gibbs Free Energy Change (\(\Delta G^o'\))**
To compute \(\Delta G^o'\) under standard conditions (pH 7 and 25°C), and given concentrations \([\text{NADH}] = 1 \, \text{mM}\) and \([\text{NAD}^+] = 2 \, \text{mM}\):
Use the Nernst equation and standard Gibbs free energy relation:
\[ \Delta G^o' = -nF \Delta E^o' \]
Where:
- \( \Delta E^o' = E^o'_{\text{(acceptor)}} - E^o'_{\text{(donor)}} \)
- \( n = \text{number of electrons transferred} \)](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F17c1e71f-55d2-4ce6-93ef-b4a233349823%2F74d730e9-c7fa-4084-aa3c-c6819454aec9%2Fvphx5p_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Oxidative Phosphorylation and NADH Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen, most living cells produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, a process occurring in the mitochondria. A key substrate that undergoes oxidation is NADH. The overall reaction for this process is:
\[ \text{NADH} + \text{H}^+ + \frac{1}{2} \text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{NAD}^+ + \text{H}_2\text{O} \]
**a. Identifying the Oxidizing Agent**
To determine the oxidizing agent in the reaction above, note that it is the substance that gains electrons. Here, \(\text{O}_2\) is the oxidizing agent because it is reduced to \(\text{H}_2\text{O}\).
**b. Calculating the Standard Electrode Potential (\(E^o'\))**
Using the half-reactions and their standard electrode potentials:
1. \( \text{NAD}^+ + \text{H}^+ + 2 \text{e}^- \rightarrow \text{NADH}, \quad E^o' = -0.320 \, \text{V} \)
2. \( \frac{1}{2} \text{O}_2 + 2 \text{H}^+ + 2 \text{e}^- \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O}, \quad E^o' = 0.816 \, \text{V} \)
**c. Calculating the Gibbs Free Energy Change (\(\Delta G^o'\))**
To compute \(\Delta G^o'\) under standard conditions (pH 7 and 25°C), and given concentrations \([\text{NADH}] = 1 \, \text{mM}\) and \([\text{NAD}^+] = 2 \, \text{mM}\):
Use the Nernst equation and standard Gibbs free energy relation:
\[ \Delta G^o' = -nF \Delta E^o' \]
Where:
- \( \Delta E^o' = E^o'_{\text{(acceptor)}} - E^o'_{\text{(donor)}} \)
- \( n = \text{number of electrons transferred} \)
Expert Solution
Step 1: oxidizing agent and answers of a and b
a.the given chemical equation is-
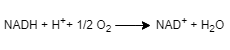
An oxidizing agent known as electron acceptor, gains electrons in a chemical reaction and gets reduced. It is generally in its higher possible oxidation state due to gaining of electrons.
In this reaction, NADH gets oxidized to NAD+ by losing electrons. So, NADH is a reducing agents.
Here, H+ + 1/2 O2, is an oxidizing agent as its oxidation state increases due to gaining of electrons in H2O
b.
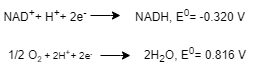
E0 for the reactions = E0 for reaction 1 +E0 for reaction 2
= - 0.320 + 0.816
= 0.496 V
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON