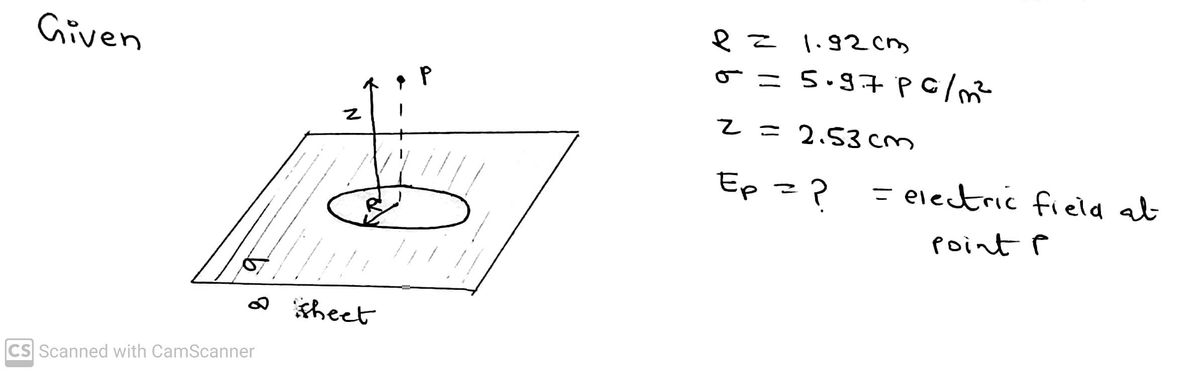
In the figure a small circular hole of radius R= 1.92 cm has been cut in the middle of an infinite, flat, nonconducting surface that has a uniform charge density o = 5.97 pC/m?. Az axis, with its origin at the hole's center, is perpendicular to the surface. What is the magnitude of the electric field at point Pat z = 2.53 cm? (Hint: See equation E = 1 - and use superposition.) 2e0 2 + R Number i 0.2687 Units N/C or V/m
In the figure a small circular hole of radius R= 1.92 cm has been cut in the middle of an infinite, flat, nonconducting surface that has a uniform charge density o = 5.97 pC/m?. Az axis, with its origin at the hole's center, is perpendicular to the surface. What is the magnitude of the electric field at point Pat z = 2.53 cm? (Hint: See equation E = 1 - and use superposition.) 2e0 2 + R Number i 0.2687 Units N/C or V/m
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
![**Description of the Image for Educational Website**
The image presents a physics problem involving an electric field on an infinite, flat, nonconducting surface with a small circular hole. Here's a breakdown of the elements involved:
### Problem Statement:
- **Surface Characteristics:**
- An infinite flat, nonconducting surface.
- Uniform charge density, \(\sigma = 5.97 \, \text{pC/m}^2\).
- **Hole Specifications:**
- Circular hole with a radius, \(R = 1.92 \, \text{cm}\).
- **Axis and Point Specification:**
- A z-axis is set with its origin at the center of the hole, perpendicular to the surface.
- The point \(P\) is located at \(z = 2.53 \, \text{cm}\).
### Objective:
- To determine the magnitude of the electric field at point \(P\).
- Equation provided for calculation:
\[
E = \frac{\sigma}{2\varepsilon_0} \left( 1 - \frac{z}{\sqrt{z^2 + R^2}} \right)
\]
- Recommendations to use the method of superposition are given in the hint.
### Graphical Description:
- The illustration depicts a green plane representing the nonconducting surface.
- A dotted circular line indicates the hole in the surface.
- The z-axis is marked, showing its perpendicular orientation to the flat plane, with a point \(P\) identified above the plane along this axis.
### Solution:
- The input field shows a calculated value of the electric field magnitude at point \(P\): \(0.2687 \, \text{N/C or V/m}\).
This setup is used to explore concepts of electric fields, charge distribution, and the effects of geometry on field calculations in electrostatics.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F42eb3f21-115e-47f2-b59c-753292f0c3d6%2F54be4e0b-cdb5-448a-9bb2-9b47c2fca0b9%2F75rzxbp_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Description of the Image for Educational Website**
The image presents a physics problem involving an electric field on an infinite, flat, nonconducting surface with a small circular hole. Here's a breakdown of the elements involved:
### Problem Statement:
- **Surface Characteristics:**
- An infinite flat, nonconducting surface.
- Uniform charge density, \(\sigma = 5.97 \, \text{pC/m}^2\).
- **Hole Specifications:**
- Circular hole with a radius, \(R = 1.92 \, \text{cm}\).
- **Axis and Point Specification:**
- A z-axis is set with its origin at the center of the hole, perpendicular to the surface.
- The point \(P\) is located at \(z = 2.53 \, \text{cm}\).
### Objective:
- To determine the magnitude of the electric field at point \(P\).
- Equation provided for calculation:
\[
E = \frac{\sigma}{2\varepsilon_0} \left( 1 - \frac{z}{\sqrt{z^2 + R^2}} \right)
\]
- Recommendations to use the method of superposition are given in the hint.
### Graphical Description:
- The illustration depicts a green plane representing the nonconducting surface.
- A dotted circular line indicates the hole in the surface.
- The z-axis is marked, showing its perpendicular orientation to the flat plane, with a point \(P\) identified above the plane along this axis.
### Solution:
- The input field shows a calculated value of the electric field magnitude at point \(P\): \(0.2687 \, \text{N/C or V/m}\).
This setup is used to explore concepts of electric fields, charge distribution, and the effects of geometry on field calculations in electrostatics.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON