In class questions: Q97: - Use the provided equation to calculate the following: KMNO, (aq) + HCI (aq) → MnCl, (aq) + Cl, (g) + H,O (1) + KCI (aq) a. The moles of H,0 that can be obtained from 15.0 mL of 0.250 M HCI. b. The volume of 0.150 M KMNO, needed to produce 0.0143 g MnCl,. c. The volume of 2.50 M HCl needed to produce 125 mL of 0.525 M KCI. 2KMNO, (aq) + 16HCI (aq) → 2MNCI, (aq) + 5Cl, (g) + 8H,0 (I) + 2KCI (aq) 01:36:12 01:59:28
In class questions: Q97: - Use the provided equation to calculate the following: KMNO, (aq) + HCI (aq) → MnCl, (aq) + Cl, (g) + H,O (1) + KCI (aq) a. The moles of H,0 that can be obtained from 15.0 mL of 0.250 M HCI. b. The volume of 0.150 M KMNO, needed to produce 0.0143 g MnCl,. c. The volume of 2.50 M HCl needed to produce 125 mL of 0.525 M KCI. 2KMNO, (aq) + 16HCI (aq) → 2MNCI, (aq) + 5Cl, (g) + 8H,0 (I) + 2KCI (aq) 01:36:12 01:59:28
Chapter24: Introduction To Spectrochemical Methods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24.18QAP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Bb Blackboard Collaborate Ultra – 1 X
Bb Collaborate - Live Tutorial Ses X
O Mail - Jenna Lewis - Outlook
G 0.615 ml to litres - Google Search x
+
8 https://au.bbcollab.com/collab/ui/session/playback
Not syncing
O Instagram
(11) Facebook
In class questions:
Q97: - Use the provided equation to calculate the following:
KMNO, (aq) + HCI (aq) → MnCl, (aq) + Cl, (g) + H,0 (1) + KCI (aq)
а.
The moles of H,0 that can be obtained from 15.0 ml of 0.250 M HCI.
b. The volume of 0.150 M KMno, needed to produce 0.0143 g MnCl,.
С.
The volume of 2.50 M HCI needed to produce 125 ml of 0.525 M KCI.
2KMNO, (aq) + 16HCI (aq) → 2MNCI, (aq) + 5Cl, (g) + 8H,0 (1) + 2KCI (aq)
01:36:12
01:59:28
[CC
9:14 AM
O Type here to search
14°C Sunny
4) ENG
9/09/2021
Expert Solution
Step 1
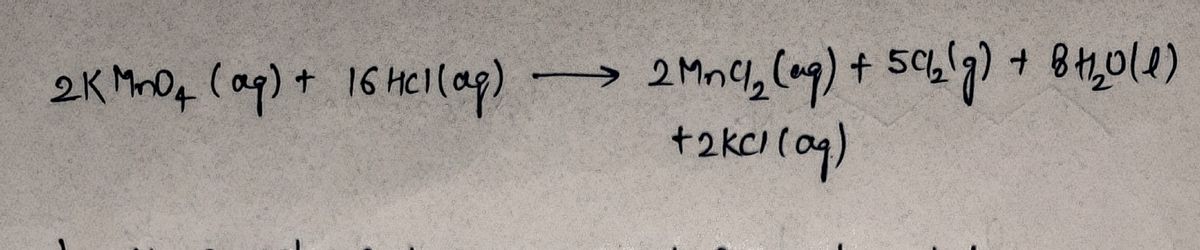
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

