In case (b) shown in (Figure 2) determine the speed of the block at s = 6 m if v = 3 m/s at s = 0.
Q: A 55 kg skateboarder wants to just make it to the upper edge of a "half-pipe" with radius r of 2.4…
A:
Q: The 510-kg uniform beam is subjected to the three external loads shown. Compute the reactions at the…
A:
Q: height ℎ, with negligible friction. At the bottom, where it is moving horizontally, it collides with…
A: a) First, we need to calculate the speed v1 of the crate of mass m1 at the bottom of the hill using…
Q: The spring connects two objects. In this case, it's the object that moves and accelerates, and the…
A:
Q: Understand what is physically happening with the spring -- the ideal version, and differences from…
A: When a spring is stretched or pulled a force is exerted by the spring which is proportional to the…
Q: A block of mass m, = 3 kg is attached to a ball of mass m2 = 5 kg by a rope passing over a light,…
A: Given that:- M1=3kg M2=5kg u=0.4 h=1.5m
Q: crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the…
A:
Q: ke it to the top of t
A:
Q: A block of mass m = 7.0 kg is given an initial speed of 4.5 m/s up the 0 =22.0° plane shown in the…
A:
Q: A steel cube with a mass of 3.0 Kg is released from rest and slides down a ramp with an incline of…
A: Given: The mass of the object is 3 kg. The angle of the inclination is 45o. The coefficient of…
Q: A 2.0 kg mass is placed against a spring of force constant 800 N/m, which has been compressed 0.22…
A:
Q: A 3 kg cart on a frictionless horizontal plane is connected with an ideal string and an ideal pulley…
A: Given,
Q: We will now determine how the 1/3 rule comes about. Consider a spring of mass ms which is attached…
A: Given,
Q: Consider a block of mass 0.220 kg attached to a spring of spring constant 120 N/m. The block is…
A: m = 0.220 kg K = 120 N/m x1 = 11.2 cm = 0.112 m
Q: A block is given an initial speed of 4.5 m/s up the 25.0 degree plane ( ignore friction). How far up…
A: Initialvelocity = V0 = 4.5 m/sangle = 25 degrees
Q: In the ballistic pendulum shown below, the block has a mass of 1.7 kg, the bullet has a mass of…
A:
Q: Tarzan grabs a vine hanging vertically from a tall tree when he is running at 9.0 m/s. (a) How high…
A:
Q: A spring is attached to an inclined plane as shown in the figure. A block of mass m is placed on the…
A: Mass = m Distance = d Initial speed = v Incline angle = θ The surface is friction-less. Let the…
Q: if k = 29 N/cm, ℓ = 9 cm, and x = 12 cm, calculate the force (in Newtons) on the object, including…
A: The force exerted by the spring on the object is proportional to the displacement (compression or…
Q: A crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the…
A: We are given spring constant and mass of crate attached to spring. We are also given compression in…
Q: In the figure below, a block of m= mass 19 kg is released from rest on a frictionless incline angled…
A: mass of block (m) = 19 kg Angle (θ) = 30ocompression (d') = 2 cm if force applied (f) = 240 N using…
Q: An inclined plane of angle θhas a spring of force constant k fastened securely at the bottom so that…
A: Let x be the compression in the spring when the block is momentarily rest. From work energy theorem…
Q: Can you help me with this problem? A block with a mass m is initially compressing a spring by x1 on…
A:
Q: You set up a ramp as depicted to practice your skateboard skills. The ramp is a wooden board L=9.0 m…
A: Given: m= 75kg h=1.5m F=76rmp L=9.0m u = 13m/s From work -energy theorem -mgh-Fl=1/2m(v2-u2)…
Q: A 250 kg roller coaster is at the top of a hill with a velocity of 5.60 m/s from a height of 70.0 m…
A: Energy Conservation: the law of energy conservation states that the total energy of an isolated…
Q: A crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the…
A: Given Data: Mass 1 (m1) = 2.4 kg.Mass 2 (m2) = 2.6 kg.Compression in spring (d) = 0.35 m.Spring…
Q: crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the…
A:
Q: Consider the track shown in the figure below. Section AB is a quadrant of a circle of radius r =…
A: Given radius = r = 2.00 m and is frictionless. From B to C is a horizontal section 3.0 m…
Q: A simple pendulum, consisting of a mass of 8.691 kg, is attached to the end of a 3.23 m length of…
A:
Q: Block A (mass 40.0 kg) and block B (mass 80.0 kg) are connected by a string of negligible mass as…
A:
The 20-kg block is subjected to the forces shown. Motion occurs to the right.
In case (b) shown in (Figure 2) determine the speed of the block at s=6 m if v= 3 m/s at s= 0.


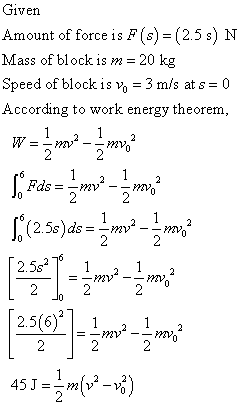
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- 8GggA uniform thin rod of length 0.6 m and mass 6.00 kg is suspended freely from one end. It is pulled to the side an angle 60 degrees and released. If friction can be ignored, what is the speed of its free end (in m/s), at the lowest point? (Could you please explain what equation I can use to find it at it's lowest point as well as a step by step formula on how to fingure out this equation. Thank you, no rush).
- As shown in the figure below, a 2.25 kg block is released from rest on a ramp of height h. When the block is released, it slides without friction to the bottom of the ramp, and then continues across a surface that is frictionless except for a rough patch of width 15.0 cm that has a coefficient of kinetic friction ?k = 0.510. Find h (in m) such that the block's speed after crossing the rough patch is 3.60 m/s. (Enter a number.)?mA glider is placed at the top of an air track that is tilted at an angle of 7.7º from the horizontal. If the glider is then let go (from rest), what is its speed at the instant it has glided 0.275 mm along the track?A 5.60-kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed of v¡ = 7.60 m/s (see figure below). %3D The block comes to rest after traveling d = 3.00 m along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 0 = 30.0° to the %3D horizontal. (a) For this motion, determine the change in the block's kinetic energy. We know an initial speed and a final speed. Are the other pieces of information relevant to this question? J (b) For this motion, determine the change in potential energy of the block-Earth system. 82.3 J (c) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). You appear to have correctly calculated the force using your incorrect results from parts (a) and (b). N (d) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? You appear to have calculated the coefficient correctly using your incorrect result from part (c).
- The pulley system below consists of two masses connected by a string of negligible mass through a massless pulley. A spring with constant k is placed so that its equilibrium position is located a distance h below the bottom of mass m2. There is no friction either in the pulley, or between the surfaces of the masses and the platform. When the two masses m₁ and m2 are released from rest, mass m2 begins falling and pulls mass m₁ up the ramp. Find an expression for the maximum compression of the spring d caused by mass m2 when it hits the spring. Your answer should be in terms of the variables given (and g). m2 MW my 0A spring gun shoots out a plastic ball at speed v. The spring is then compressed twice the distance it was on the first shot.Need in typing only or word file (no handwriting and no image, NO Plagiarism)
- Find the maximum height of y4. I keep getting 0.324. but it keeps saying it is incorrectWhat is the maximum speed vmax of the block during this motion? Find the acceleration a of the block as a function of time. Find Kmax, the maximum kinetic energy of the block.A miniature hill in a child’s toy collection is shown below. When released at A, a mass m slides down the path shown below, reaching the bottom (B) with a speed of vB. Assume that the hill has negligible friction. The block then slides along the rough horizontal surface a distance d before coming to rest at C. When solving parts (a) and (b): Write the useful description about what is known and unknown. Write down the physics principle or strategy you will use. Symbolically solve for the unknowns (a) Calculate the height of the hill using m=230.0 g and vB = 3.8 m/s (b) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction along the horizontal surface if d=14 m? Hint: Treat the motion down the hill and the motion down the rough horizontal surface as two distinct problems. What physics concepts can you apply for each?