In an exit poll, for which the sample size was 3130, suppose that 65% of all voters voted for a recall. Answer the following questions. a. Define a binary random variable taking values 0 and 1 that represent the vote for a particular voter (1 = vote for recall). State its probability distribution. Choose the sentence below that best describes the probability distribution. OA. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 1096 people voted for recall and 2035 did not. B. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.65 and P(0) = 0.35. OC. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 2035 people voted for recall and 1096 did not. OD. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.35 and P(0) = 0.65. b. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the proportion of the 3130 people in the sample who voted for the recall. mean = 0.65 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) standard deviation = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
In an exit poll, for which the sample size was 3130, suppose that 65% of all voters voted for a recall. Answer the following questions. a. Define a binary random variable taking values 0 and 1 that represent the vote for a particular voter (1 = vote for recall). State its probability distribution. Choose the sentence below that best describes the probability distribution. OA. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 1096 people voted for recall and 2035 did not. B. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.65 and P(0) = 0.35. OC. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 2035 people voted for recall and 1096 did not. OD. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.35 and P(0) = 0.65. b. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the proportion of the 3130 people in the sample who voted for the recall. mean = 0.65 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) standard deviation = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
2.

Transcribed Image Text:In an exit poll, for which the sample size was 3130, suppose that 65% of all voters voted for a recall. Answer the following questions.
a. Define a binary random variable taking values 0 and 1 that represent the vote for a particular voter (1 = vote for recall). State its probability distribution. Choose the sentence below that best
describes the probability distribution.
A. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 1096 people voted for recall and 2035 did not.
B. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.65 and P(0) = 0.35.
C. For each random sample of 3130 people, about 2035 people voted for recall and 1096 did not.
D. The binary random variable is the vote for the recall with yes or no. For each observation, P(1) = 0.35 and P(0) = 0.65.
b. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the proportion of the 3130 people in the sample who voted for the recall.
mean = 0.65 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
standard deviation = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
Step 1
(b )
Obtain the mean of the sampling distribution of the proportion of the 3130 people in the sample who voted for the recall.
The mean of the sampling distribution of the proportion of the 3130 people in the sample who voted for the recall is obtained below as follows:
Let the random variable X follows binomial distribution with
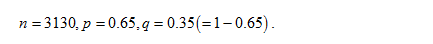
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman