Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
ChapterP: Preliminary Concepts
SectionP.CT: Test
Problem 1CT
Related questions
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem: Finding Angle Measures in an Isosceles Trapezoid**
**Question:**
If \(ABCD\) is an isosceles trapezoid, find \( m < A \).
**Diagram:**
The diagram is of an isosceles trapezoid \(ABCD\) with the following notations:
- \(D\) is at the bottom left, \(A\) is above \(D\), \(C\) is at the bottom right, and \(B\) is above \(C\).
- The non-parallel sides \(AD\) and \(BC\) are of equal length, implying it is an isosceles trapezoid.
- \( \angle D \) is labeled as \(3x-12\).
- \( \angle C \) is labeled as \(2x+1\).
**Options:**
a. 113
b. 27
c. 153
d. 41
**Solution:**
To solve this problem, consider the properties of an isosceles trapezoid:
1. In an isosceles trapezoid, the base angles are equal.
2. The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is \(360^\circ\).
The next steps would involve setting up equations based on these properties to find \(x\) and then determine the measure of \( \angle A \). However, the necessary steps and calculations are not provided in the image. For a complete solution, detailed algebraic manipulations are required which might typically follow the given diagram setup in an educational context.
**Note:** This layout is meant for an educational website, providing a problem setup and steps toward a solution in a structured manner.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
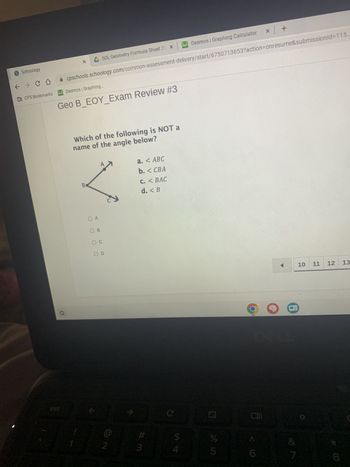
Transcribed Image Text:**Geo B_EOY_Exam Review #3**
**Question:**
Which of the following is NOT a name of the angle below?
**Image Description:**
A diagram is presented showing three points labeled A, B, and C. The points are connected by lines forming angles at each point. The specific angle of interest is shown to be at point B.
**Options:**
a. ∠ABC
b. ∠CBA
c. ∠BAC
d. ∠B
**Explanation:**
- ∠ABC: This notation suggests the angle formed with point B as the vertex and points A and C as the arms.
- ∠CBA: This notation also suggests an angle with point B as the vertex, but with the order of points switched.
- ∠BAC: This notation suggests an angle with point A as the vertex, which is not consistent with the angle indicated in the diagram.
- ∠B: This notation simply refers to the angle at point B without specifying the other points.
Correct Answer:
c. ∠BAC
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, geometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning