![### Ideal Gas Law Problem
**Problem Statement:**
If 21.5 mol of an ideal gas is at 4.81 atm at 91.60 °C, what is the volume of the gas?
**Formula:**
We can use the Ideal Gas Law equation to solve for volume \( V \):
\[ PV = nRT \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the pressure (in atmospheres)
- \( V \) is the volume (in liters, L)
- \( n \) is the number of moles
- \( R \) is the ideal gas constant (0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K))
- \( T \) is the temperature (in Kelvin, K)
**Solution:**
1. Convert the temperature from Celsius to Kelvin:
\[ T(K) = 91.60 °C + 273.15 = 364.75 \, K \]
2. Substitute the known values into the Ideal Gas Law formula:
\[ P = 4.81 \, \text{atm} \]
\[ n = 21.5 \, \text{mol} \]
\[ R = 0.0821 \, \text{L·atm/(mol·K)} \]
\[ T = 364.75 \, \text{K} \]
3. Solve for \( V \):
\[ V = \frac{nRT}{P} \]
\[ V = \frac{(21.5 \, \text{mol}) \times (0.0821 \, \text{L·atm/(mol·K)}) \times (364.75 \, \text{K})}{4.81 \, \text{atm}} \]
**Calculation Box:**
\[ V = \boxed{\text{_______}} \, L \]
**Conclusion:**
Enter the calculated volume in the box provided to find out the volume of the gas under the given conditions.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F2531879c-adde-4e1b-ab06-85ed93219951%2F5a63e7be-22f6-47c8-8f70-560bf9aa44e8%2F1aq6lsi.png&w=3840&q=75)
The law combining all thermodynamic variables together through an expression (PV=nRT) is recognized as "ideal gas law". This is based on theory that gases possess negligible inter-molecular interactions.
Given:
The pressure of the gas is 4.81 atm.
The temperature of the gas is 91.60 degrees C.
The number of moles of gas is 21.5 mol.
The expression of the ideal gas equation is shown below.
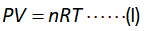
Here,
The pressure of the gas is “P”.
The volume of the gas is “V”.
The number of moles of the gas is “n”.
The gas constant is “R”.
The temperature of the gas is “T”.
The value of gas constant (R) is 0.0821 L-atm/mol-K.
The conversion of temperature from Celsius to Kelvin is shown below.
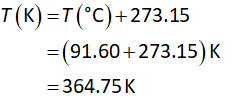
Substitute the known values in equation (I)

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









